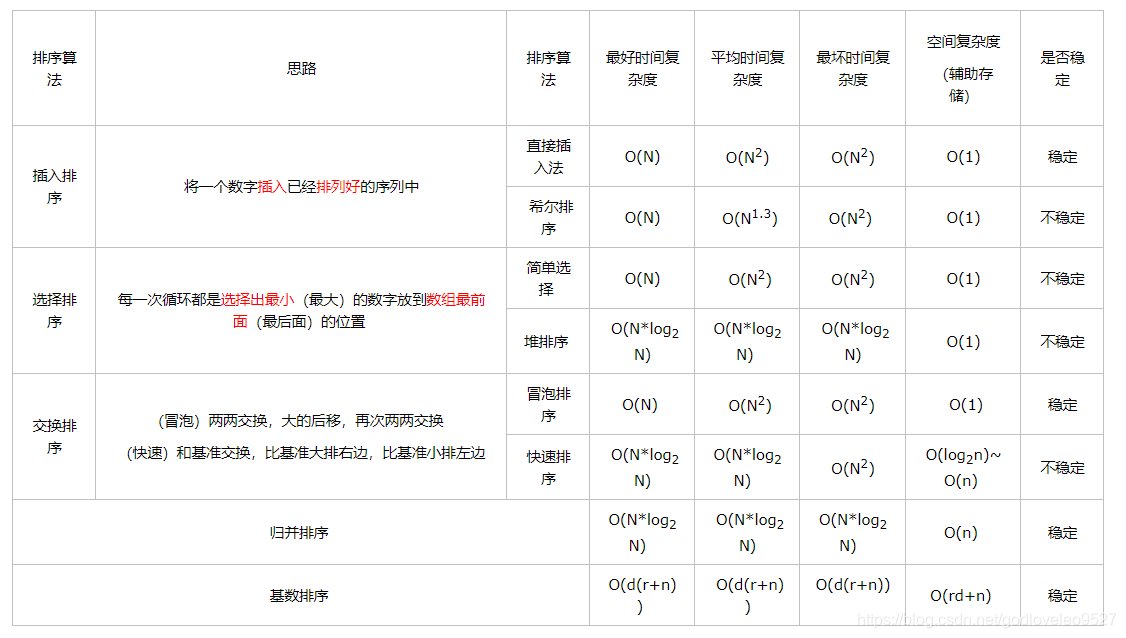
在要排序的一组数中,假设前面(n-1) [n>=2] 个数已经是排好顺序的,现在要把第n个数插到前面的有序数中,使得这n个数也是排好顺序的。如此反复循环,直到全部排好顺序。 直接插入排序的平均复杂度为O(n²),最坏时间复杂度:O(n²),空间复杂度:O(1),没有分配内存。 针对直接插入排序下的效率问题,有人对此进行了改进与升级,这就是现在的希尔排序。希尔排序,也称递减增量排序算法,是插入排序的一种更高效的改进版本。希尔排序是非稳定排序算法。 1.数的个数为length,i=length/2,将下标差值为i的数分为一组,构成有序序列。 2.再取i=i/2 ,将下标差值为i的数分为一组,构成有序序列。 3.重复第二步,直到k=1执行简单插入排序。 思路: 希尔排序举例: (1)首先确定每一组序列的下标的间隔,循环每次需要的间隔:int i = length/2; i >0 ; i /= 2 (2)然后将每一组序列中元素进行插入排序,第二组第一个插入的数字是第一组第一个插入数字之后的那个数组,从i之后每个数字都要进行插入排序,就是插入的序列是各自不同的序列,不是一个一个子序列循环,而是在一个循环中for (int j=i;j<length;j++)完成所有子序列的插入排序。 (3)直到i=0为止。 希尔排序的平均时间复杂度为O(n²),空间复杂度O(1) 。 基本原理如下:对于给定的一组记录,经过第一轮比较后得到最小的记录,然后将该记录的位置与第一个记录的位置交换;接着对不包括第一个记录以外的其他记录进行第二次比较,得到最小记录并与第二个位置记录交换;重复该过程,直到进行比较的记录只剩下一个为止。 简单选择排序的时间复杂度为O(n²) n个节点的完全二叉树array[0,…,n-1],最后一个节点n-1是第(n-1-1)/2个节点的孩子。对第(n-1-1)/2个节点为根的子树调整,使该子树称为堆。 对于大根堆,调整方法为:若【根节点的关键字】小于【左右子女中关键字较大者】,则交换。 之后向前依次对各节点((n-2)/2 – 1)~ 0为根的子树进行调整,看该节点值是否大于其左右子节点的值,若不是,将左右子节点中较大值与之交换,交换后可能会破坏下一级堆,于是继续采用上述方法构建下一级的堆,直到以该节点为根的子树构成堆为止。 反复利用上述调整堆的方法建堆,直到根节点。 时间复杂度:建堆:o(n),每次调整o(log n),故最好、最坏、平均情况下:o(n*logn); 打个小guang告,搜索拼duoduo店铺: Boush杂货铺 一次冒泡将序列中从头到尾所有元素两两比较,将最大的放在最后面。 将剩余序列中所有元素再次两两比较,将最大的放在最后面。 重复第二步,直到只剩下一个数。 冒泡排序的最好时间复杂度为O(n),最坏时间复杂度为O(n²),平均时间复杂度为O(n²),空间复杂度为O(1),它是一种稳定的排序算法。 快速排序使用分治策略来把一个序列(list)分为两个子序列(sub-lists)。步骤为: 递归到最底部时,数列的大小是零或一,也就是已经排序好了。这个算法一定会结束,因为在每次的迭代(iteration)中,它至少会把一个元素摆到它最后的位置去。 虽然 快排的时间复杂度达到了 O(n²),但是在大多数情况下都比平均时间复杂度为 O(n logn) 的排序算法表现要更好。 归并排序(MERGE-SORT)是利用归并的思想实现的排序方法,该算法采用经典的分治(divide-and-conquer)策略(分治法将问题分(divide)成一些小的问题然后递归求解,而治(conquer)的阶段则将分的阶段得到的各答案”修补”在一起,即分而治之)。 可以看到这种结构很像一棵完全二叉树,本文的归并排序我们采用递归去实现(也可采用迭代的方式去实现)。分阶段可以理解为就是递归拆分子序列的过程,递归深度为log2n。 归并排序是稳定排序,它也是一种十分高效的排序,能利用完全二叉树特性的排序一般性能都不会太差。java中Arrays.sort()采用了一种名为TimSort的排序算法,就是归并排序的优化版本。从上文的图中可看出,每次合并操作的平均时间复杂度为O(n),而完全二叉树的深度为|log2n|。总的平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。而且,归并排序的最好,最坏,平均时间复杂度均为O(nlogn)。 归并排序是稳定排序,它也是一种十分高效的排序,能利用完全二叉树特性的排序一般性能都不会太差。java中Arrays.sort()采用了一种名为TimSort的排序算法,就是归并排序的优化版本。从上文的图中可看出,每次合并操作的平均时间复杂度为O(n),而完全二叉树的深度为|log2n|。总的平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。而且,归并排序的最好,最坏,平均时间复杂度均为O(nlogn)。 引用: https://www.cnblogs.com/mensan/p/10570050.html https://www.cnblogs.com/jyroy/p/11248691.html https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6194356.html https://www.jianshu.com/p/8340dfaea3af
– 1.基本思路
– 2.代码实现
– 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
– 1.基本思路
– 2.代码实现
– 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
– 1.基本思路
– 2.代码实现
– 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
– 1.基本思路
– 2.代码实现
– 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
– 1.基本思路
– 2.代码实现
– 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
– 1.基本思路
– 2.代码实现
– 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
– 1.基本思路
– 2.代码实现
– 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
– 1.基本思路
– 2.代码实现
– 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度八大排序算法
一、直接插入
1.基本思路
2.代码实现
public static void insertSort(int[] data) { int temp; for(int i = 1;i < data.length; i++){// 取第i个数,插入前边的有序的序列 temp = data[i]; int j; for(j = i - 1; j>=0; j--) {// 从第i-1的位置上开始比较 if(data[j] > temp) {// 若前面的数大,则往后挪一位 data[j+1] = data[j]; } else { break;// 否则,说明要插入的数比较大 } } data[j+1] = temp;// 找到这个位置,插入数据 } } 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
二、希尔排序
1.基本思路
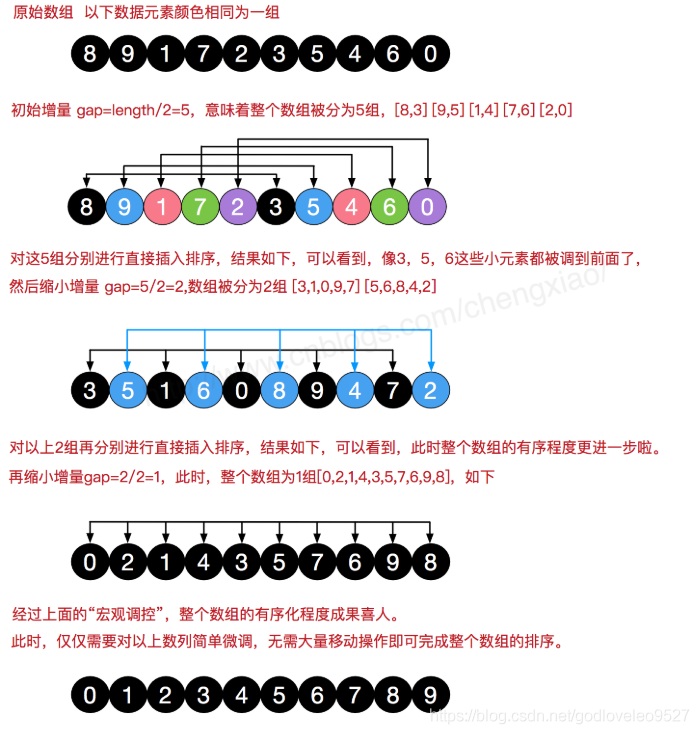
2.代码实现
public static void shellSort(int[] array) { int length = array.length; for (int i = length / 2; i > 0; i /= 2) {//序列的间隔,一直到间隔为一,这时候就只有一个子序列 for (int j = i; j < length; j++) {//从i之后每个数字都要进行插入排序,就是插入的序列是各自不同的序列 int temp = array[j];//里面就是直接插入算法 int k; for (k = j - i; k >= 0; k -= i) {//实现各个数字插入排序到不同的序列中,直到间隔为1的时候,只有一个序列,就是完全的一个直接插入排序 if (temp < array[k]) { array[k + i] = array[k]; } else { break; } } array[k + i] = temp;//把数字插入到位置上 } } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
三、简单选择
1.基本思路
2.代码实现
public static void selectSort(int[] array) { int len = array.length; for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {//确定每次开始的位置 int min = array[i];//设定开始数字为最小的值最小值 int flag = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {//把最小值存放到min,从开始数字向后一个个和min比较,再把最小值存放到min if (min > array[j]) { min = array[j]; flag = j; } } if (flag != i) { array[flag] = array[i]; array[i] = min; } } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
四、堆排序
1.基本思路
任意一节点指针 i: 父节点:i==0 ? null : (i-1)/2 左孩子:2*i + 1 右孩子:2*i + 2
n个关键字序列array[0,...,n-1],当且仅当满足下列要求:(0 <= i <= (n-1)/2) ① array[i] <= array[2*i + 1] 且 array[i] <= array[2*i + 2]; 称为小根堆; ② array[i] >= array[2*i + 1] 且 array[i] >= array[2*i + 2]; 称为大根堆;
①将存放在array[0,...,n-1]中的n个元素建成初始堆; ②将堆顶元素与堆底元素进行交换,则序列的最大值即已放到正确的位置; ③将数组中array[0,...,n-1]前n-1个元素再次形成大根堆,再重复第②③步,直到堆中仅剩下一个元素为止。 2.代码实现
/** * 大顶堆排序 * @param array */ public static void maxHeapSort(int[] array) { int i; int len = array.length; // 构建大顶堆 for (i = len / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) { adjustMaxHeap(array, i, len); } // 堆顶是最大值,交换堆顶和最后一个数,再重新调整最大堆,下一次循环 i-- for (i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--) { int temp = array[0]; array[0] = array[i]; array[i] = temp; adjustMaxHeap(array, 0, i); } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static void adjustMaxHeap(int[] a, int pos, int len) { int temp; int child; for (temp = a[pos]; 2 * pos + 1 < len; pos = child) { // 数组从0开始,r(i)>=r(2i) r(i)>=r(2i+1) 对应 pos => 2 * pos + 1 和 2 * pos +2 child = 2 * pos + 1; // 有右孩子,且右孩子数值更大 if (child + 1 < len && a[child] < a[child + 1]) { child++; } // 最大的孩子大于根节点 if (a[child] > temp) { a[pos] = a[child]; } else { break; } } a[pos] = temp; } 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
五、冒泡排序
物美价廉,你值得拥有1.基本思路
2.代码实现
/** * @author fupeng * 冒泡排序优化第二版 * 第一版优化增加flag标记,没有数字交换直接return,最优时间复杂度O(n) * 第二版优化,增加tempPostion记录内循环最后一次交换的位置,来缩减内循环的次数 */ public static void bubbleSort(int[] array) { int len = array.length - 1; int temp; // 开辟一个临时空间, 存放交换的中间值 int tempPostion = 0; // 记录最后一次交换的位置 // 要遍历的次数 for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) { int flag = 1; // 设置一个标志位 // 依次的比较相邻两个数的大小,遍历一次后,把数组中第i小的数放在第i个位置上 for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) { // 比较相邻的元素,如果前面的数大于后面的数,交换 if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) { temp = array[j + 1]; array[j + 1] = array[j]; array[j] = temp; flag = 0; // 发生交换,标志位置0 tempPostion = j; // 记录交换的位置 } } len = tempPostion; // 把最后一次交换的位置给len,来缩减内循环的次数 if (flag == 1) {// 如果没有交换过元素,则已经有序 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); return; } } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
六、快速排序
1.基本思路
2.代码实现
public static void quickSort(int[] array) { sort(array, 0, array.length - 1); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static void sort(int[] a, int low, int high) { int i = low; int j = high; if (a.length <= 1) { return; } if (i >= j) { return; } int index = a[i]; while (i < j) { while (i < j && a[j] >= index) j--; if (a[j] < index) a[i++] = a[j]; while (i < j && a[i] <= index) i++; if (a[i] > index) a[j--] = a[i]; } a[i] = index; sort(a, low, i - 1); sort(a, i + 1, high); } 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
七、归并排序
1.基本思路
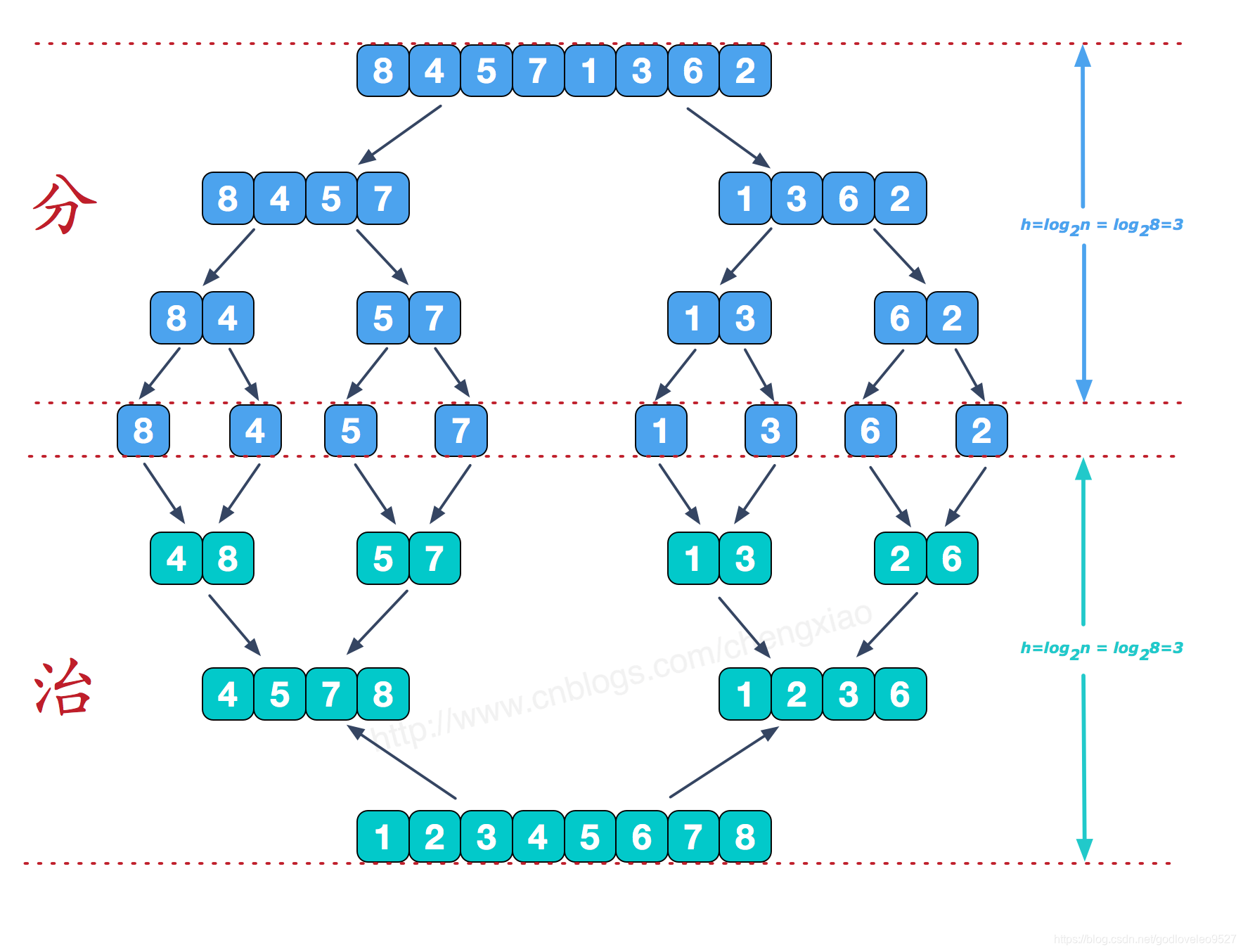
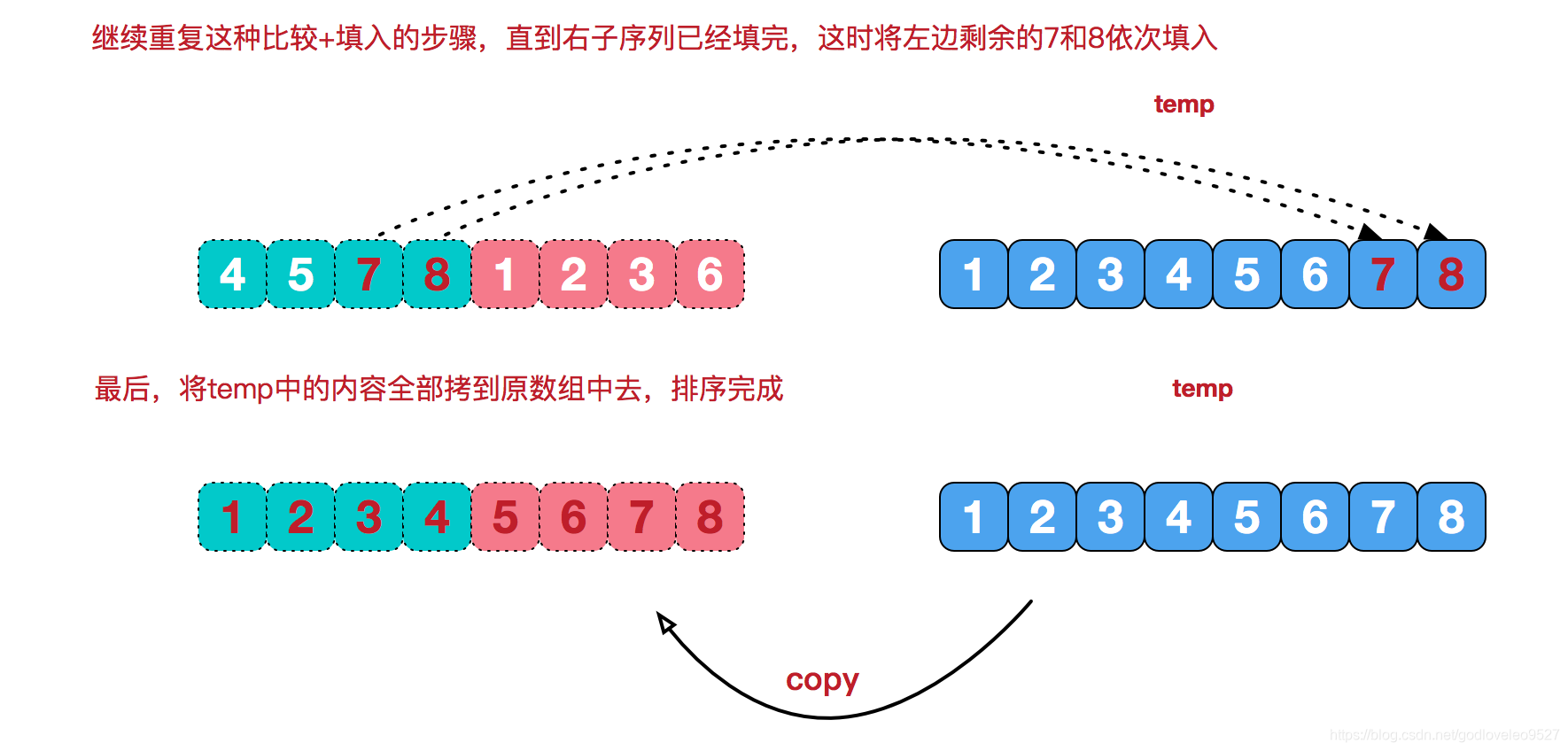
再来看看治阶段,我们需要将两个已经有序的子序列合并成一个有序序列,比如上图中的最后一次合并,要将[4,5,7,8]和[1,2,3,6]两个已经有序的子序列,合并为最终序列[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8],来看下实现步骤。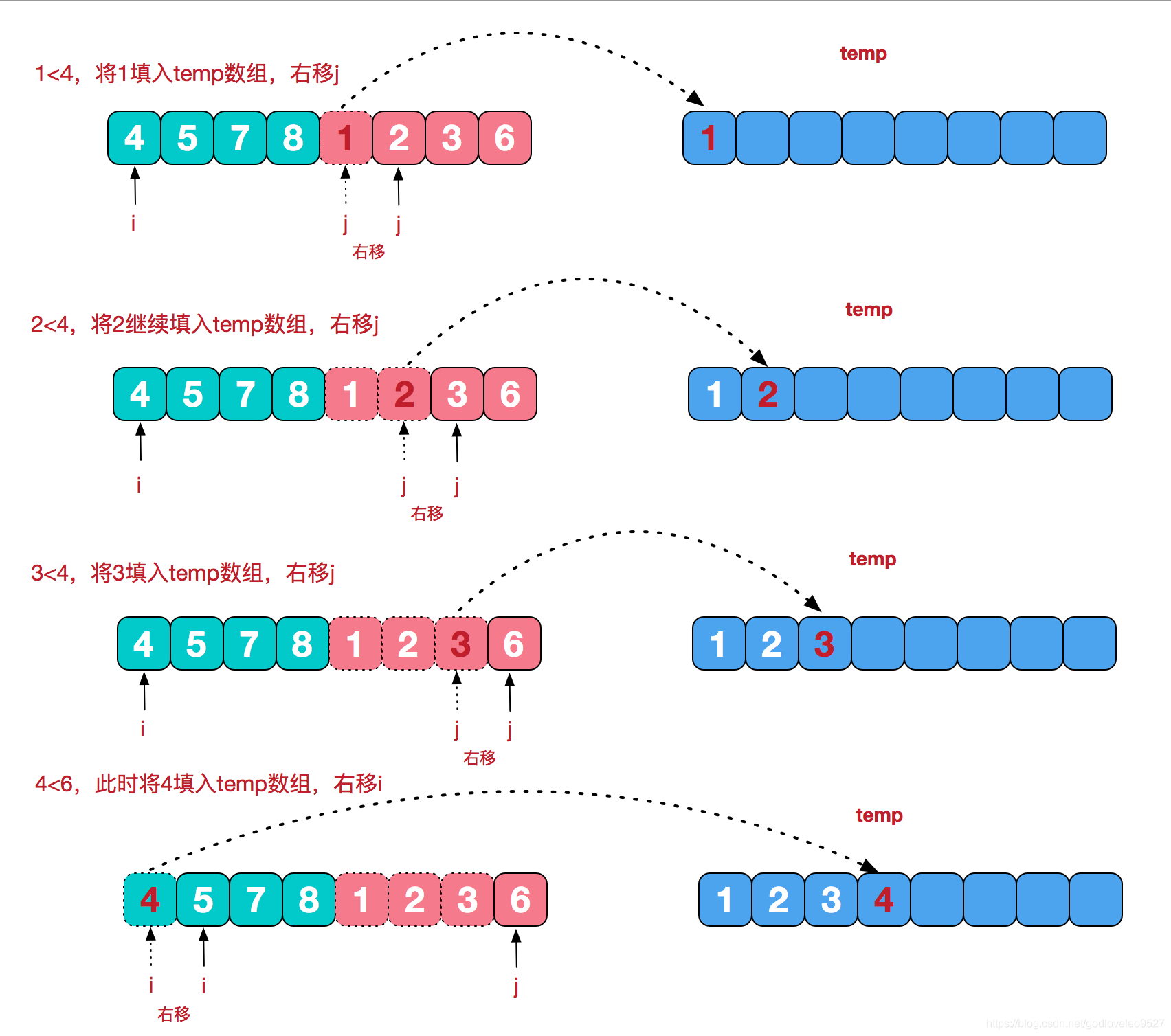
2.代码实现
public static void mergeSort(int[] array) { int[] temp = new int[array.length];// 在排序前,先建好一个长度等于原数组长度的临时数组,避免递归中频繁开辟空间 mergeSort(array, 0, array.length-1, temp); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static void mergeSort(int[] arr, int left, int right, int []temp) { if(left < right) { int mid = (left+right) / 2; mergeSort(arr, left, mid, temp);// 左边归并排序,使得左子序列有序 mergeSort(arr, mid+1, right, temp);// 右边归并排序,使得右子序列有序 merge(arr, left, mid, right, temp);// 将两个有序子数组合并操作 } } private static void merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right, int[] temp) { int i = left;// 左序列指针 int j = mid+1;// 右序列指针 int t = 0;// 临时数组指针 while (i <= mid && j <= right) { if(arr[i] <= arr[j]) { temp[t++] = arr[i++]; } else { temp[t++] = arr[j++]; } } while(i <= mid) {// 将左边剩余元素填充进temp中 temp[t++] = arr[i++]; } while(j <= right) {// 将右序列剩余元素填充进temp中 temp[t++] = arr[j++]; } t = 0; // 将temp中的元素全部拷贝到原数组中 while(left <= right) { arr[left++] = temp[t++]; } } 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
八、基数排序
1.基本思路

2.代码实现
public static void radixSort(int[] array) { ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> queue = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) { queue.add(new ArrayList<>());// 创建一个基数从0---9 每个数字上都是一个list } // 找到最大值,并判断最大值是几位数 int max = array[0]; for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) { if (max < array[i]) { max = array[i]; } } int time = 0; while (max > 0) { max /= 10; time++; } for (int i = 0; i < time; i++) {// 循环每一个位数(个位、十位、百位) for (int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) {// 循环数组,取每一个值 int x = array[j] % (int) Math.pow(10, i + 1) / (int) Math.pow(10, i); ArrayList<Integer> queue3 = queue.get(x); queue3.add(array[j]); queue.set(x, queue3); } int count = 0; for (int k = 0; k < 10; k++) { while (queue.get(k).size() > 0) { ArrayList<Integer> queue4 = queue.get(k); array[count] = queue4.get(0); queue4.remove(0); count++; } } } } 3.时间复杂度和空间复杂度
总结
本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)