分析在 在使用 的方式获得动态代理对象。如果是 这里我们看到最底层还是调用了JDK动态代理方式生成代理对象。我们知道代理模式一般是将原类进行增强,比如说增加了日志,增加了事务,增加了切面等。那么这里增加了什么呢?我们看看这个增强对象 动态代理的原理这里不多说,可以参考本人的另外一篇文章Spring Aop JDK动态代理实现原理分析(源码) 深入讨论,简而言之就是代理对象在程序运行时才生产,这个对象实现了目标接口(这里是 我们前面的文章已经分析了在启动阶段, ms中存在一些sql的信息,保存sql语句,参数类型等,接下来就需要了解如何通过传入的参数,动态创建sql。 至此一条完整的sql就执行完了,还有很多细节我们可以深入研究,但是这里就不详细展开了。后续继续跟进。
目的
sql执行时,mybatis的底层做了哪些处理,为啥mapper接口能执行?这就是本文的目标,mapper执行过程都有哪些关键信息。
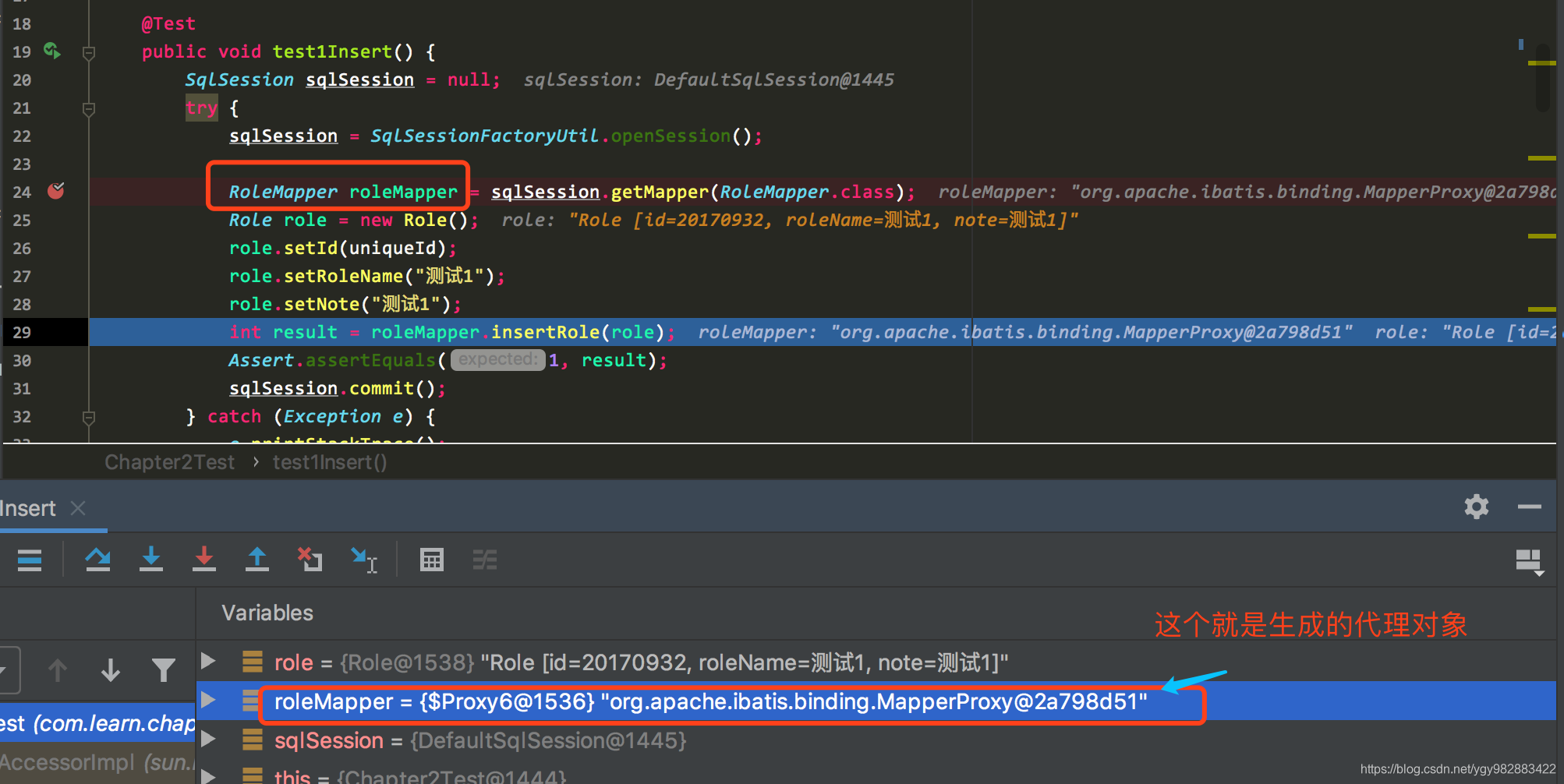
如果需要了解mybaits启动流程,整体架构情况可以看另外一篇mybatis 启动流程分析(原理)mapper接口的动态代理实现mapper对象的时候,我们只是定义了接口,并没有实现类,但是在实际项目我们却是直接使用接口的。这里就涉及到动态代理的相关知识。本文的分析中,我们是通过RoleMapper roleMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(RoleMapper.class); mybaits和spring结合使用,那么这些mapper接口的动态代理过程就交给了spring来控制。我们只需要在用的地方通过注解@Autowire引入mapper即可。下图展示了动态代理实现的调用流程。

我们看看实现动态代理的部分核心代码 // 1 public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); return newInstance(mapperProxy); } // 2 protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { //用JDK自带的动态代理生成映射器 return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); } MapperProxy/** * 映射器代理,代理模式 * */ public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L; private final SqlSession sqlSession; private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache; public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) { this.sqlSession = sqlSession; this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; this.methodCache = methodCache; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //代理以后,所有Mapper的方法调用时,都会调用这个invoke方法 //并不是任何一个方法都需要执行调用代理对象进行执行,如果这个方法是Object中通用的方法(toString、hashCode等)无需执行 if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { try { return method.invoke(this, args); } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } } //这里优化了,去缓存中找MapperMethod final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); //执行 return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); } //去缓存中找MapperMethod private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) { MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method); if (mapperMethod == null) { //找不到才去new mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()); methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod); } return mapperMethod; } } mapper对象),并且持有MapperProxy的引用,在几乎每个方法中都会调用下MapperProxy的invoke方法。下图证明了mapper接口生成了动态代理对象。
如何执行
mybatis是如何将mapper里面的所有接口转成mappedstatement存储到Configuration对象中保存。
而且存储在一个map中,key就是我们的方法签名。所有我们需要从map中拿到对应的mappedstatement。//从Configuration对象中拿到对应的mappedStatement对象 MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
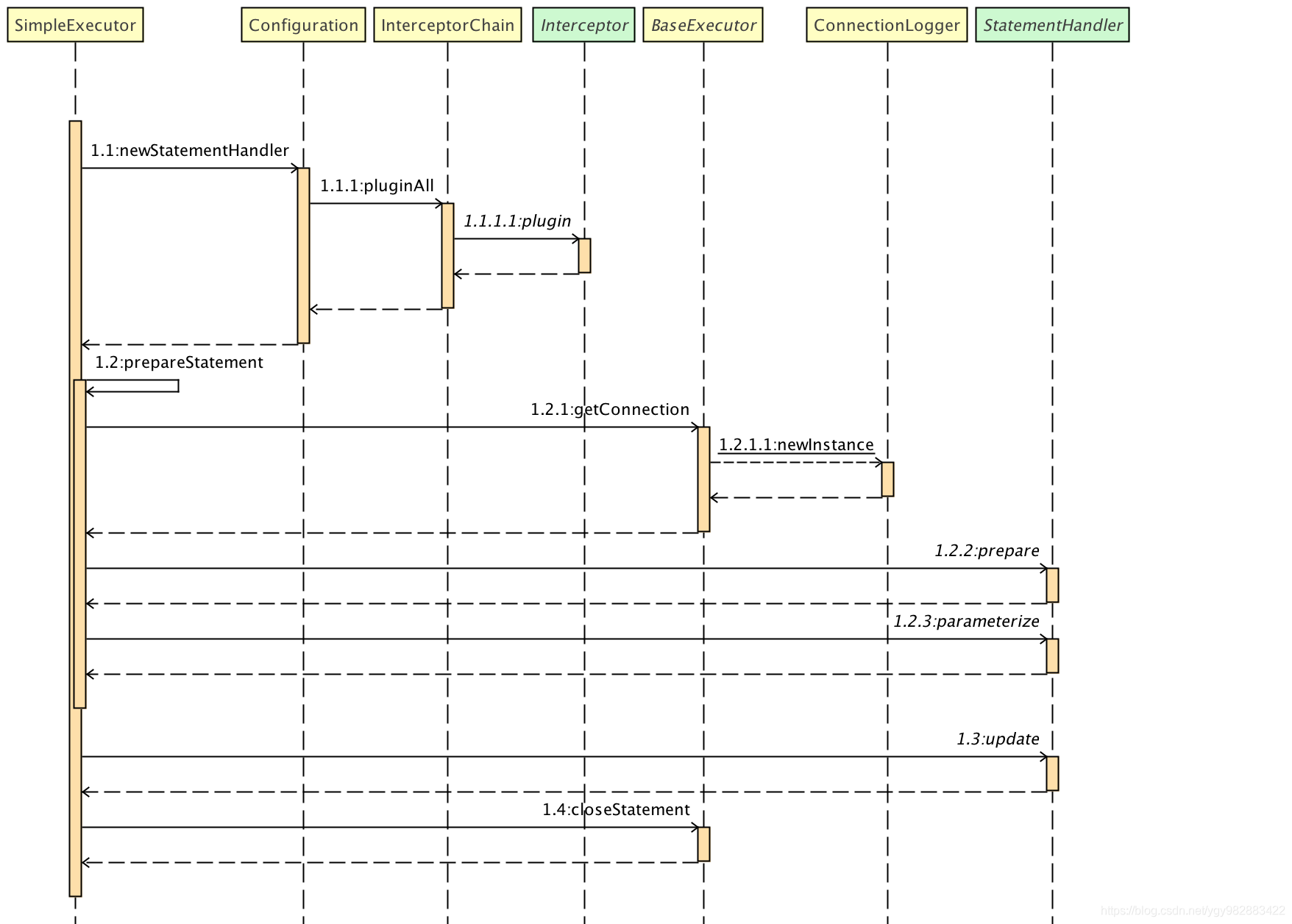
这里一共3个大步骤
StatementHandler //创建语句处理器 public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { //创建路由选择语句处理器 StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); //插件在这里插入 statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler); return statementHandler; }
Statement包括获得数据库连接、参数设置等 public Statement prepare(Connection connection) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql()); Statement statement = null; try { //实例化Statement statement = instantiateStatement(connection); //设置超时 setStatementTimeout(statement); //设置读取条数 setFetchSize(statement); return statement; } catch (SQLException e) { closeStatement(statement); throw e; } catch (Exception e) { closeStatement(statement); throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e); } } 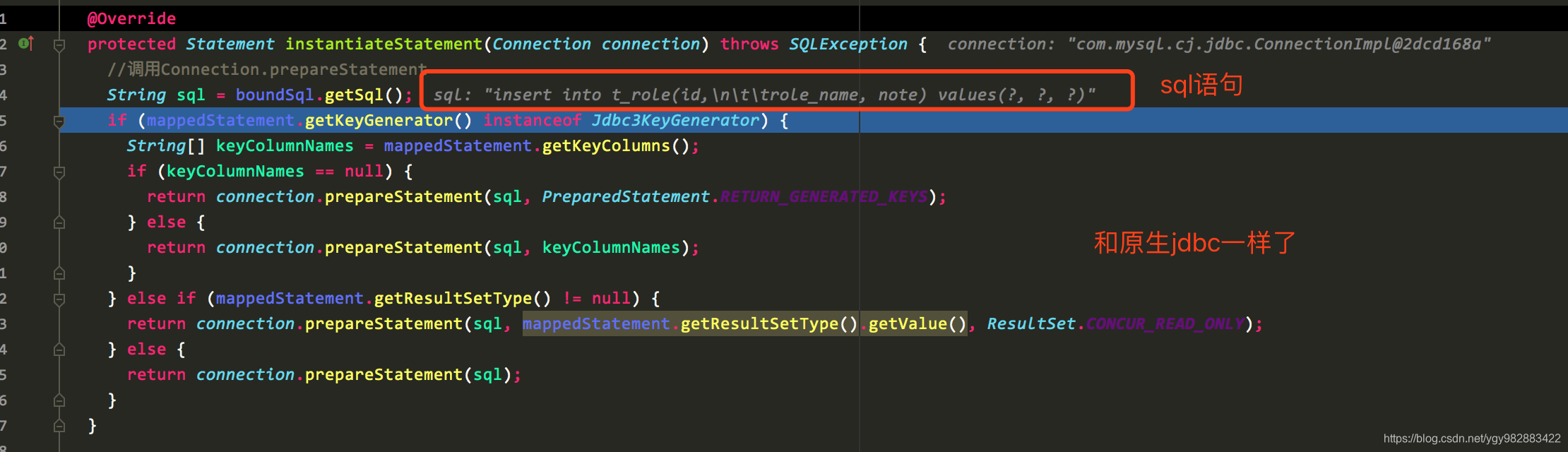
然后是给preparedStatement设置参数,这个和我们jdbc一样的顺序 //设置参数 @Override public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException { ErrorContext.instance().activity("setting parameters").object(mappedStatement.getParameterMap().getId()); List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); if (parameterMappings != null) { //循环设参数 for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) { ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i); if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) { //如果不是OUT,才设进去 Object value; String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { // issue #448 ask first for additional params //若有额外的参数, 设为额外的参数 value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); } else if (parameterObject == null) { //若参数为null,直接设null value = null; } else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) { //若参数有相应的TypeHandler,直接设object value = parameterObject; } else { //除此以外,MetaObject.getValue反射取得值设进去 MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject); value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName); } TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler(); JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType(); if (value == null && jdbcType == null) { //不同类型的set方法不同,所以委派给子类的setParameter方法 jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull(); } typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType); } } } }
@Override public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException { //调用PreparedStatement.execute和PreparedStatement.getUpdateCount PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement; ps.execute(); int rows = ps.getUpdateCount(); Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject(); KeyGenerator keyGenerator = mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator(); keyGenerator.processAfter(executor, mappedStatement, ps, parameterObject); return rows; }
本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)