这篇文章通过对花鸢尾属植物进行分类,来学习如何利用实际数据构建一个感知机模型,(文末附GD和SGD参数更新手推公式)。 目录 Iris数据集是常用的分类实验数据集,由Fisher, 1936收集整理。Iris也称鸢尾花卉数据集,是一类多重变量分析的数据集。数据集包含150个数据样本,分为3类,每类50个数据,每个数据包含4个属性。可通过花萼长度,花萼宽度,花瓣长度,花瓣宽度4个属性预测鸢尾花卉属于(Setosa,Versicolour,Virginica)三个种类中的哪一类。 iris以鸢尾花的特征作为数据来源,常用在分类操作中。该数据集由3种不同类型的鸢尾花的各50个样本数据构成。其中的一个种类与另外两个种类是线性可分离的,后两个种类是非线性可分离的。 该数据集包含了4个属性: & Sepal.Length(花萼长度),单位是cm; & Sepal.Width(花萼宽度),单位是cm; & Petal.Length(花瓣长度),单位是cm; & Petal.Width(花瓣宽度),单位是cm; 种类:Iris Setosa(山鸢尾)、Iris Versicolour(杂色鸢尾),以及Iris Virginica(维吉尼亚鸢尾)。 结果: 分类误差: 分类结果:
一、数据集
二、需要导入的库
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap #from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron import Perceptron as perceptron_class三、读取数据集
df = pd.read_csv('https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/iris/iris.data', header=None) df.tail() #抽取出前100条样本,这正好是Setosa和Versicolor对应的样本,我们将Versicolor对应的数据作为类别1,Setosa对应的作为-1。 # 对于特征,我们抽取出sepal length和petal length两维度特征,然后用散点图对数据进行可视化 #We extract the first 100 class labels that correspond to 50 Iris-Setosa and 50 Iris-Versicolor flowers. y = df.iloc[0:100, 4].values print(y) y = np.where(y == 'Iris-setosa', -1, 1)#满足条件(condition),输出x,不满足输出y。 print(y) X = df.iloc[0:100, [0, 2]].values print(X) print(X.shape,y.shape)#(100,2) (100,)
['Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-setosa' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor' 'Iris-versicolor'] [-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1] [[5.1 1.4] [4.9 1.4] [4.7 1.3] [4.6 1.5] [5. 1.4] [5.4 1.7] [4.6 1.4] [5. 1.5] [4.4 1.4] [4.9 1.5] [5.4 1.5] [4.8 1.6] [4.8 1.4] [4.3 1.1] [5.8 1.2] [5.7 1.5] [5.4 1.3] [5.1 1.4] [5.7 1.7] [5.1 1.5] [5.4 1.7] [5.1 1.5] [4.6 1. ] [5.1 1.7] [4.8 1.9] [5. 1.6] [5. 1.6] [5.2 1.5] [5.2 1.4] [4.7 1.6] [4.8 1.6] [5.4 1.5] [5.2 1.5] [5.5 1.4] [4.9 1.5] [5. 1.2] [5.5 1.3] [4.9 1.5] [4.4 1.3] [5.1 1.5] [5. 1.3] [4.5 1.3] [4.4 1.3] [5. 1.6] [5.1 1.9] [4.8 1.4] [5.1 1.6] [4.6 1.4] [5.3 1.5] [5. 1.4] [7. 4.7] [6.4 4.5] [6.9 4.9] [5.5 4. ] [6.5 4.6] [5.7 4.5] [6.3 4.7] [4.9 3.3] [6.6 4.6] [5.2 3.9] [5. 3.5] [5.9 4.2] [6. 4. ] [6.1 4.7] [5.6 3.6] [6.7 4.4] [5.6 4.5] [5.8 4.1] [6.2 4.5] [5.6 3.9] [5.9 4.8] [6.1 4. ] [6.3 4.9] [6.1 4.7] [6.4 4.3] [6.6 4.4] [6.8 4.8] [6.7 5. ] [6. 4.5] [5.7 3.5] [5.5 3.8] [5.5 3.7] [5.8 3.9] [6. 5.1] [5.4 4.5] [6. 4.5] [6.7 4.7] [6.3 4.4] [5.6 4.1] [5.5 4. ] [5.5 4.4] [6.1 4.6] [5.8 4. ] [5. 3.3] [5.6 4.2] [5.7 4.2] [5.7 4.2] [6.2 4.3] [5.1 3. ] [5.7 4.1]] (100, 2) (100,)四、数据散点图可视化
plt.scatter(X[:50, 0], X[:50, 1],color='red', marker='o', label='setosa') plt.scatter(X[50:100, 0], X[50:100, 1],color='blue', marker='x', label='versicolor') plt.xlabel('sepal length') plt.ylabel('petal length') plt.legend(loc='upper left') plt.show()
五、利用感知机模型进行线性分类
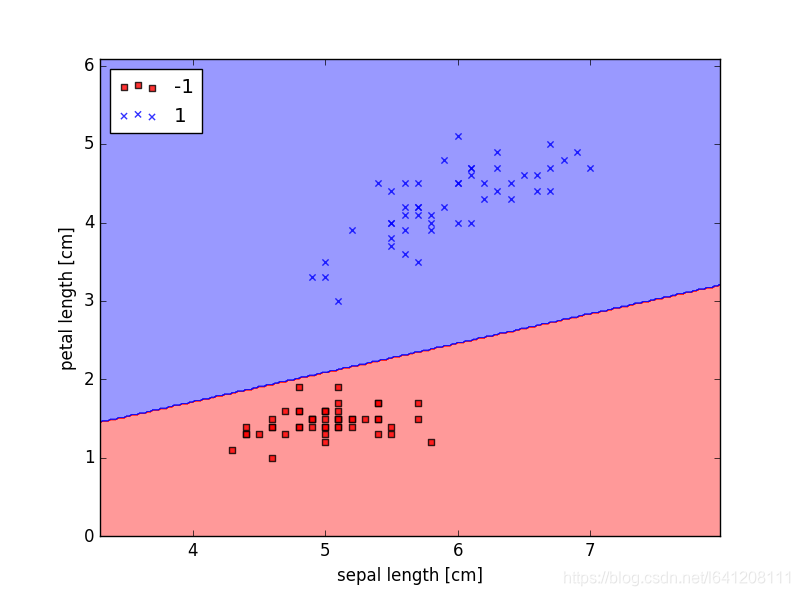
#这里是对于感知机模型进行训练 ppn = perceptron_class.Perceptron(eta=0.1, n_iter=10) ppn.fit(X, y) #画出分界线 #To train our perceptron algorithm, plot the misclassification error plt.plot(range(1,len(ppn.errors_) + 1), ppn.errors_, marker='o') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Number of misclassifications') plt.show() #Visualize the decision boundaries for 2D datasets def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, resolution=0.02): # setup marker generator and color map markers = ('s', 'x', 'o', '^', 'v') colors = ('red', 'blue', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan') cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))]) # plot the decision surface x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1 x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1 xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution), np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution)) Z = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T) Z = Z.reshape(xx1.shape) print(xx1) plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap=cmap) plt.xlim(xx1.min(), xx1.max()) plt.ylim(xx2.min(), xx2.max()) # plot class samples for idx, cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)):#除其中重复的元素,并按元素由大到小返回一个新的无元素重复的元组或者列表 plt.scatter(x=X[y == cl, 0], y=X[y == cl, 1],alpha=0.8, c=cmap(idx), marker=markers[idx],label=cl) plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier=ppn) plt.xlabel('sepal length [cm]') plt.ylabel('petal length [cm]') plt.legend(loc='upper left') plt.show()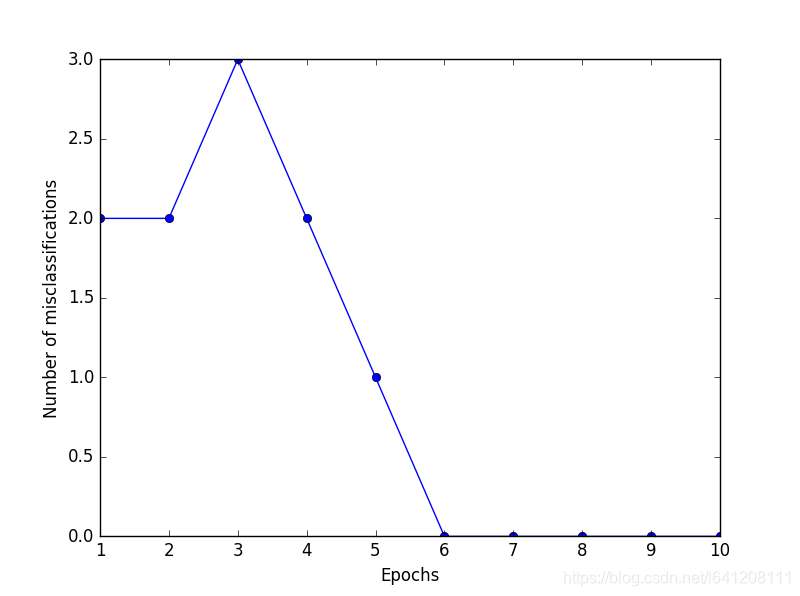
六、不同学习率损失可视化对比
#Adaptive linear neurons and the convergence of learning Implementing an Adaptive Linear Neuron in Python fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(8,4)) ada1 = perceptron_class.AdalineGD(n_iter=10, eta=0.01).fit(X,y) ax[0].plot(range(1, len(ada1.cost_) + 1), np.log10(ada1.cost_), marker='o') ax[0].set_xlabel('Epochs') ax[0].set_ylabel('log(Sum-squared-error)') ax[0].set_title('Adaline - Learning rate 0.01') ada2 = perceptron_class.AdalineGD(n_iter=10, eta=0.0001).fit(X,y) ax[1].plot(range(1, len(ada2.cost_) + 1), ada2.cost_, marker='o') ax[1].set_xlabel('Epochs') ax[1].set_ylabel('Sum-squared-error') ax[1].set_title('Adaline - Learning rate 0.0001') plt.show()
七、归一化后分类
#standardization X_std = np.copy(X) X_std[:,0] = (X_std[:,0] - X_std[:,0].mean()) / X_std[:,0].std() X_std[:,1] = (X_std[:,1] - X_std[:,1].mean()) / X_std[:,1].std() ada = perceptron_class.AdalineGD(n_iter=15, eta=0.01) ada.fit(X_std, y) plot_decision_regions(X_std, y, classifier=ada) plt.title('Adaline - Gradient Descent') plt.xlabel('sepal length [standardized]') plt.ylabel('petal length [standardized]') plt.legend(loc='upper left') # plt.show() plt.plot(range(1, len(ada.cost_) + 1), ada.cost_, marker='o') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Sum-squared-error') plt.show()
八、随机梯度下降
#Large scale machine learning and stochastic gradient descent ada = perceptron_class.AdalineSGD(n_iter=15, eta=0.01, random_state=1) ada.fit(X_std, y) plot_decision_regions(X_std, y, classifier=ada) plt.title('Adaline - Stochastic Gradient Descent') plt.xlabel('sepal length [standardized]') plt.ylabel('petal length [standardized]') plt.legend(loc='upper left') plt.show() plt.plot(range(1, len(ada.cost_) + 1), ada.cost_, marker='o') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Average Cost') plt.show()

九、完整的代码
import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap #from sklearn.linear_model import Perceptron import Perceptron as perceptron_class df = pd.read_csv('https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/iris/iris.data', header=None) df.tail() #抽取出前100条样本,这正好是Setosa和Versicolor对应的样本,我们将Versicolor对应的数据作为类别1,Setosa对应的作为-1。 # 对于特征,我们抽取出sepal length和petal length两维度特征,然后用散点图对数据进行可视化 #We extract the first 100 class labels that correspond to 50 Iris-Setosa and 50 Iris-Versicolor flowers. y = df.iloc[0:100, 4].values print(y) y = np.where(y == 'Iris-setosa', -1, 1)#满足条件(condition),输出x,不满足输出y。 print(y) X = df.iloc[0:100, [0, 2]].values print(X) print(X.shape,y.shape)#(100,2) (100,) plt.scatter(X[:50, 0], X[:50, 1],color='red', marker='o', label='setosa') plt.scatter(X[50:100, 0], X[50:100, 1],color='blue', marker='x', label='versicolor') plt.xlabel('sepal length') plt.ylabel('petal length') plt.legend(loc='upper left') plt.show() #这里是对于感知机模型进行训练 ppn = perceptron_class.Perceptron(eta=0.1, n_iter=10) ppn.fit(X, y) #画出分界线 #To train our perceptron algorithm, plot the misclassification error plt.plot(range(1,len(ppn.errors_) + 1), ppn.errors_, marker='o') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Number of misclassifications') plt.show() #Visualize the decision boundaries for 2D datasets def plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier, resolution=0.02): # setup marker generator and color map markers = ('s', 'x', 'o', '^', 'v') colors = ('red', 'blue', 'lightgreen', 'gray', 'cyan') cmap = ListedColormap(colors[:len(np.unique(y))]) # plot the decision surface x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1 x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1 xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, resolution), np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, resolution)) Z = classifier.predict(np.array([xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).T) Z = Z.reshape(xx1.shape) print(xx1) plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, Z, alpha=0.4, cmap=cmap) plt.xlim(xx1.min(), xx1.max()) plt.ylim(xx2.min(), xx2.max()) # plot class samples for idx, cl in enumerate(np.unique(y)):#除其中重复的元素,并按元素由大到小返回一个新的无元素重复的元组或者列表 plt.scatter(x=X[y == cl, 0], y=X[y == cl, 1],alpha=0.8, c=cmap(idx), marker=markers[idx],label=cl) plot_decision_regions(X, y, classifier=ppn) plt.xlabel('sepal length [cm]') plt.ylabel('petal length [cm]') plt.legend(loc='upper left') plt.show() #Adaptive linear neurons and the convergence of learning Implementing an Adaptive Linear Neuron in Python fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(8,4)) ada1 = perceptron_class.AdalineGD(n_iter=10, eta=0.01).fit(X,y) ax[0].plot(range(1, len(ada1.cost_) + 1), np.log10(ada1.cost_), marker='o') ax[0].set_xlabel('Epochs') ax[0].set_ylabel('log(Sum-squared-error)') ax[0].set_title('Adaline - Learning rate 0.01') ada2 = perceptron_class.AdalineGD(n_iter=10, eta=0.0001).fit(X,y) ax[1].plot(range(1, len(ada2.cost_) + 1), ada2.cost_, marker='o') ax[1].set_xlabel('Epochs') ax[1].set_ylabel('Sum-squared-error') ax[1].set_title('Adaline - Learning rate 0.0001') plt.show() #standardization X_std = np.copy(X) X_std[:,0] = (X_std[:,0] - X_std[:,0].mean()) / X_std[:,0].std() X_std[:,1] = (X_std[:,1] - X_std[:,1].mean()) / X_std[:,1].std() ada = perceptron_class.AdalineGD(n_iter=15, eta=0.01) ada.fit(X_std, y) plot_decision_regions(X_std, y, classifier=ada) plt.title('Adaline - Gradient Descent') plt.xlabel('sepal length [standardized]') plt.ylabel('petal length [standardized]') plt.legend(loc='upper left') # plt.show() plt.plot(range(1, len(ada.cost_) + 1), ada.cost_, marker='o') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Sum-squared-error') plt.show() #Large scale machine learning and stochastic gradient descent ada = perceptron_class.AdalineSGD(n_iter=15, eta=0.01, random_state=1) ada.fit(X_std, y) plot_decision_regions(X_std, y, classifier=ada) plt.title('Adaline - Stochastic Gradient Descent') plt.xlabel('sepal length [standardized]') plt.ylabel('petal length [standardized]') plt.legend(loc='upper left') plt.show() plt.plot(range(1, len(ada.cost_) + 1), ada.cost_, marker='o') plt.xlabel('Epochs') plt.ylabel('Average Cost') plt.show()
import numpy as np from numpy.random import seed class Perceptron(object): """Perceptron classifier. Parameters ------------ eta : float Learning rate (between 0.0 and 1.0) n_iter : int Passes over the training dataset. Attributes ----------- w_ : 1d-array Weights after fitting. errors_ : list Number of misclassifications (updates) in each epoch. """ def __init__(self, eta=0.01, n_iter=10): self.eta = eta self.n_iter = n_iter def fit(self, X, y): """Fit training data. Parameters ---------- X : {array-like}, shape = [n_samples, n_features] Training vectors, where n_samples is the number of samples and n_features is the number of features. y : array-like, shape = [n_samples] Target values. Returns ------- self : object """ self.w_ = np.zeros(1 + X.shape[1]) self.errors_ = [] for _ in range(self.n_iter): errors = 0 for xi, target in zip(X, y): update = self.eta*(target - self.predict(xi)) self.w_[1:] += update*xi self.w_[0] += update errors += int(update != 0.0) self.errors_.append(errors) return self def net_input(self, X): """Calculate net input""" return np.dot(X, self.w_[1:]) + self.w_[0] def predict(self, X): """Return class label after unit step""" return np.where(self.net_input(X) >= 0.0, 1, -1) class AdalineGD(object): """ADAptive LInear NEuron classifier. Parameters ------------- eta : float Learning rate (between 0.0 and 1.0) n_iter : int Passes over the training dataset. Attributes ------------- w_ : 1d-array Weights after fitting. errors_ : list Number of misclassifications in every epoch. """ def __init__(self, eta=0.01, n_iter=50): self.eta = eta self.n_iter = n_iter def fit(self, X, y): """ Fit training data. Parameters ------------ X : {array-like5}, shape = [n_samples, n_features] Training vectors, where n_samples is the number of samples and n_features is the number of features. y : array-like, shape = [n_samples] Target values. Returns ------------ self : object """ self.w_ = np.zeros(1 + X.shape[1]) self.cost_ = [] for i in range(self.n_iter): output = self.net_input(X) errors = (y - output) self.w_[1:] += self.eta * X.T.dot(errors) self.w_[0] += self.eta * errors.sum() cost = (errors**2).sum() / 2.0 self.cost_.append(cost) return self def net_input(self, X): """Calculate net input""" return np.dot(X, self.w_[1:]) + self.w_[0] def activation(self, X): """Compute linear activation""" return self.net_input(X) def predict(self, X): """Return class label after unit step""" return np.where(self.activation(X) >= 0.0, 1, -1) class AdalineSGD(object): """ADAptive LInear NEuron classifier. Parameters ------------ eta : float Learning rate (between 0.0 and 1.0) n_iter : int Passes over the training dataset. Attributes ------------ w_ : 1d-array Weights after fitting. cost_ : list Number of misclassifications in every epoch. shuffle : bool (default: True) Shuffles training data every epoch if True to prevent cycles. random_state : int (default: None) Set random state for shuffling and initializing the weights. """ def __init__(self, eta=0.01, n_iter=10, shuffle=True, random_state=None): self.eta = eta self.n_iter = n_iter self.w_initialized = False self.shuffle = shuffle if random_state: seed(random_state) def fit(self, X, y): """Fit training data. Parameters ------------ X : {array-like}, shape = [n_samples, n_features] Training vector, where n_samples is the number of samples and n_features is the number of features. y: arrary-like, shape = [n_samples] Target values. Returns ------------ self : object """ self._initialize_weights(X.shape[1]) self.cost_ = [] for i in range(self.n_iter): if self.shuffle: X, y = self._shuffle(X, y) cost = [] for xi, target in zip(X, y): cost.append(self._update_weights(xi, target)) avg_cost = sum(cost)/len(y) self.cost_.append(avg_cost) return self def partial_fit(self, X, y): """Fit training data without reinitializing the weights""" if not self.w_initialized: self._initialize_weights(X.shape[1]) if y.ravel().shape[0] > 1: for xi, target in zip(X, y): self._update_weights(xi, target) else: self._update_weights(X, y) return self def _shuffle(self, X, y): """Shuffle training data""" r = np.random.permutation(len(y)) return X[r], y[r] def _initialize_weights(self, m): """Initialize weighs to zeros""" self.w_ = np.zeros(1+m) self.w_initialized = True def _update_weights(self, xi, target): """Apply Adaline learning rule to update the weights""" output = self.net_input(xi) error = (target - output) self.w_[1:] += self.eta*xi.dot(error) self.w_[0] += self.eta*error cost = 0.5 * error**2 return cost def net_input(self, X): """Calculate net input""" return np.dot(X, self.w_[1:]) + self.w_[0] def activation(self, X): """Compute linear activation""" return self.net_input(X) def predict(self, X): """Return class label after unit step""" return np.where(self.activation(X) >= 0.0, 1, -1) 十、公式推导:


本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)