因为最近要考ocp(全英文考试,所以下文也会中英夹杂,侧重oracle标准。),又要把大学学过的数据库捡起来。特开此文整理基础sql语句语法和注意事项。 一人书写这么多内容,难免有错,欢迎大家留言。 1970年,美国IBM研究中心的E.F.Codd提出关系模型,拉开了未来五十年经久不衰的关系数据库的帷幕。 不看懂也没关系,也不影响语法学习。 CHAR: 固定长度字符串 最大长度2000 bytes RAW: 固定长度的二进制数据 最大长度2000 bytes 可存放多媒体图象声音等 CREATE TABLE Statement • You specify: • Confirm table creation: Constraints约束 KEY Constraint: Keywords含有外键从表 Violating Constraint违反约束 Creating a Table Using a Subquery使用子查询,用另外表添加数据 • Match the number of specified columns to the number of subquery columns. ALTER TABLE Statement修改表的结构 • The new column becomes the last column:所有值自动设置为空 • A change to the default value affects only subsequent insertions to the table. SET UNUSED Option某个字段设置不可用 Dropping a Table删除表 创建在一个表上的视窗,不存放数据,逻辑视窗 Create view创建视图 · Create the EMPVU80 view,which contains details of the employees in department 80: · Describe the structure of the view by using the SQL*Plus DESCRIBE command: DESCRIBE emp vu 80 The subquery can contain complex SELECT syntax A sequence: 引用序列号NEXTVAL and CURRVAL Pseudocolun · You must be the owner or have the ALTER privilege for the sequence. DROP SEQUENCE dept_dept id_seq; An index:树状结构,单独存储, 复杂的对象设置一个简单的名称
基础sql语句大全
前言
所有示例代码均来自oracle官方教材。参考资料:数据库系统教程和oracle提供的官方教材。SQL语句概述
SQL原来是指“结构化查询语句Structured Query Language”,经过不断发展,已经不表示任何具体的缩写含义,成为一个通用标准。
SQL主要包括:
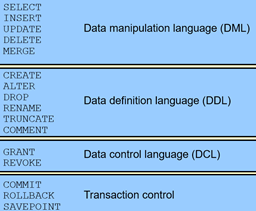
1. DDL(数据定义语言 data definition language ):定义基本表,视图,索引等结构。
2. DML(数据操作语言 data manipulation language ):分为数据查询和数据更新(插入、删除、修改)
3. DCL(数据权限管理语句data control language):对基本表和视图的授权、完整性规则的描述。事务控制语句也可以包括在这里。
4. 事务控制管理语句(transaction control)
5. 嵌入式SQL的使用
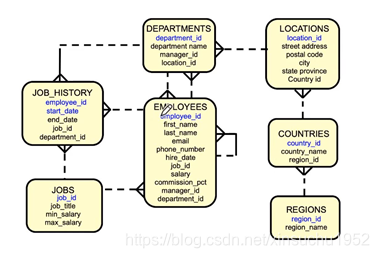
示例所用E-R图
E-R图:Human Resources (HR) Schema人力资源计划
Oracle常用数据类型规定
VARCHAR2: 可变长度的字符串 最大长度4000 bytes 可做索引的最大长度749
NCHAR: 根据字符集而定的固定长度字符串 最大长度2000 bytes
NVARCHAR2: 根据字符集而定的可变长度字符串 最大长度4000 bytes
DATE: 日期(日-月-年) DD-MM-YY(HH-MI-SS) 经过严格测试,无千虫问题
LONG :超长字符串 最大长度2G(231-1) 足够存储大部头著作
NUMBER(P,S) 数字类型 P为总位数,S为小数位数
LONG RAW: 可变长度的二进制数据 最大长度2G 同上
CLOB: 字符数据 最大长度4G
BLOB: 二进制数据 最大长度4G
BFILE: 存放在数据库外的二进制数据 最大长度4G
ROWID: 数据表中记录的唯一行号 10 bytes ********.****.****格式,*为0或1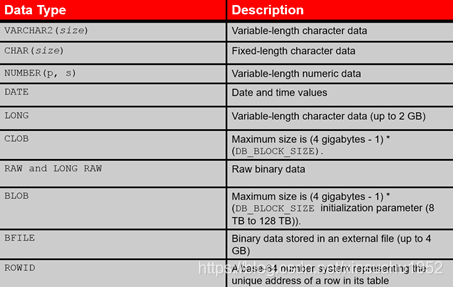
第一章 DDL:Data Definition Language
Naming Rules命名规则
Table names and column names must:
• Begin with a letter字母开始
• Be 1–30 characters long
• Contain only A–Z, a–z, 0–9, _, $, and #【命名允许使用字符】
• Not duplicate the name of another object owned by the same user【同一用户下不同对象不能命相同的名】
• Not be an Oracle server–reserved word不使用oracle保留字【例如table等常见英文单词】基本表的创建、修改、删除
• You must have:
– The CREATE TABLE privilege
– A storage areaCREATE TABLE [schema.指定用户]table (column datatype [DEFAULT expr][, ...]) [CONSTRAINT constraint_name] constraint_type,; //段名+数据类型+约束名+约束类型
– The table name
– The column name, column data type, and column size
• Create the table:例子CREATE TABLE dept//表名 (deptno NUMBER(2)//字段名和数据类型, dname VARCHAR2(14), loc VARCHAR2(13) NOT NULL,//非空 create_date DATE DEFAULT SYSDATE); DESCRIBE 表名;//查看表的结构(字段和类型)
• Constraints enforce rules at the table level.
• Constraints ensure the consistency and integrity of the database.
• The following constraint types are valid:
– NOT NULL非空
– UNIQUE唯一
– PRIMARY KEY主键
– FOREIGN KEY外键
– CHECK校验
• View a constraint in the data dictionary.数据字典中查看
• You can name a constraint or the Oracle server generates a name by using the SYS_Cn format.约束命名
• Create a constraint at either of the following times:创建约束的时间
– At the same time as the creation of the table在创建表的同时
– After the creation of the table创建表之后//Example of a column-level constraint CREATE TABLE employees( employee_id NUMBER(6) CONSTRAINT emp_emp_id_pk约束名称 PRIMARY KEY, first_name VARCHAR2(20), ...); //Example of a table-level constraint: CREATE TABLE employees( employee_id NUMBER(6), first_name VARCHAR2(20), job_id VARCHAR2(10) NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT emp_emp_id_pk PRIMARY KEY (EMPLOYEE_ID指定));
CREATE TABLE employees( employee_id NUMBER(6), last_name VARCHAR2(25) NOT NULL, email VARCHAR2(25),//unique约束 salary NUMBER(8,2), commission_pct NUMBER(2,2), hire_date DATE NOT NULL, CONSTRAINT emp_email_uk UNIQUE(email)字段名;
CREATE TABLE employees( employee_id NUMBER(6), last_name VARCHAR2(25) NOT NULL, email VARCHAR2(25), salary NUMBER(8,2), commission_pct NUMBER(2,2), hire_date DATE NOT NULL, department_id NUMBER(4), CONSTRAINT emp_dept_fk FOREIGN KEY (department_id)//外键:关系数据库的参照完整性,定义从表 REFERENCES departments(department_id),引用主表 CONSTRAINT emp_email_uk UNIQUE(email));
• FOREIGN KEY: Defines the column in the child table at the table-constraint level
• REFERENCES: Identifies the table and column in the parent table
• ON DELETE CASCADE: Deletes the dependent rows in the child table when a row in the parent table is deleted
主表删除时,主从表都删除记录
• ON DELETE SET NULL: Converts dependent foreign key values to null从表改为空,主表删除
5. CHECK Constraint校验约束
• It defines a condition that each row must satisfy.
• The following expressions are not allowed:
– References to CURRVAL, NEXTVAL, LEVEL, and ROWNUM pseudocolumns
– Calls to SYSDATE, UID, USER, and USERENV functions
– Queries that refer to other values in other rowssalary NUMBER(2) CONSTRAINT emp_salary_min CHECK (salary > 0);//使用整数校验 UPDATE employees//更新从表employess数据 SET department_id = 55//报错291,55在主表department中未出现 WHERE department_id = 110; You cannot delete a row that contains a primary key that is used as a foreign key in another table. DELETE FROM departments删除主表中数据 WHERE department_id = 60;错误
• Create a table and insert rows by combining the CREATE TABLE statement and the AS subquery option.CREATE TABLE table [(column, column...)] AS subquery;匹配字段
• Define columns with column names and default values.Creating a Table Using a Subquery CREATE TABLE dept80 AS SELECT employee_id, last_name,salary*12 ANNSAL, hire_date FROM employees WHERE department_id = 80;
Use the ALTER TABLE statement to:
• Add a new column
• Modify an existing column definition
• Define a default value for the new column
• Drop a column
• Rename a column
• Change table to read-only status
Use the ALTER TABLE statement to add, modify, or drop columns:
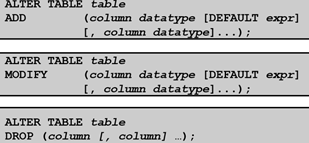
Adding a Column增加字段
• You use the ADD clause to add columns:ALTER TABLE dept80 ADD (job_id VARCHAR2(9));
Modifying a Column修改字段
• You can change a column’s data type, size, and default value.ALTER TABLE dept80 MODIFY (last_name VARCHAR2(30));
Dropping a Column删除字段
Use the DROP COLUMN clause to drop columns that you no longer need from the table:ALTER TABLE dept80 MODIFY (last_name VARCHAR2(30));
• You use the SET UNUSED option to mark one or more columns as unused.
• You use the DROP UNUSED COLUMNS option to remove the columns that are marked as unused.
• You can specify the ONLINE keyword to indicate that DML operations on the table will be allowed while marking the column or columns UNUSED.
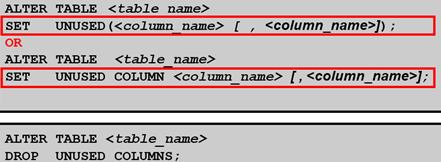
Read-Only Tables只读表
You can use the ALTER TABLE syntax to:
• Put a table in read-only mode, which prevents DDL or DML changes during table maintenance
• Put the table back into read/write modeALTER TABLE employees READ ONLY;//设定为只读表,不允许修改 --perform table maintenance and then return table back to read/write mode ALTER TABLE employees READ WRITE;
• Moves a table to the recycle bin
• Removes the table and all its data entirely if the PURGE clause is specified
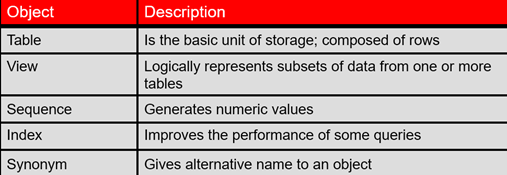
• Invalidates dependent objects and removes object privileges on the tableDROP TABLE 表名; //结构和数据全部删除,存在回收站,还可以闪回操作 View视图
Advantage of views:
to restrict data access
to make complex queries easy
to provide data independence
to present different views of the same data
两种视图:简单视图和复杂视图
You embed a subquery in the CREATE VIEW statement:CREATE [OR REPLACE] [FORCE|NOFORCE] VIEW view识图名 [(alias[, alias] ...) ] AS subquey子查询 [WITH CHECK OPTION [CONSTRAINT constraint] ] [WITH READ ONLY [CONSTRAINT constraint]]; CREATE VIEW empvu80 AS SELECT employee_id, last_name,salary FROM employees WHERE department id=80;
Modify view 修改视图:
create or replace view 识图名 as 子查询
· Modify the EMPVU80 view by using a CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW clause.Add an alias for each columnname:
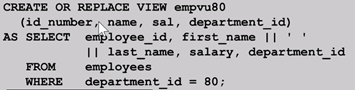
· Column aliases in the CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW clause are listed in the same order as the columns in the subquery.
Complex view 复杂视图:使用子查询连接
Create a complex view that contains group functions to display values from two tables:

不建议使用DML语句修改视图,WITH READ ONLY;
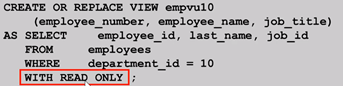
· You can usually perform DML operations on simple views.
· You can not remove a row if the view contains the following:
You can not modify data in a view if it contains:
· Group functions
· A GROUP BY clause
· The DISTINCT keyword
· The pseudo column ROWNUM keyword
· Columns defined by expressions
You can not add data through a view if the view includes:
· The pseudo column ROWNUM keyword
· Group functions
· A GROUP BY clause
· The DISTINCT keyword
· Columns defined by expressions
· NOT NULL columns in the base tables that are not selected by the viewDrop view 视图名;删除视图 Sequence序列号
Can automatically generate unique numbers
is a shareable object
Can be used to create a primary key value
Replaces application code
Speeds up the efficiency of accessing sequence values when cached in memoryCREATE SEQUENCE 序列名 [INCREMENT BY n]增长值 [START WITH n]第一个值 [(MAXVALUE n | NOMAXVALUE)]最大 [(MINVALUE n | NOMINVALUE)]是否包含最小 [(CYCLE | NOCYCLE) ]循环使用,不建议 [(CACHE n | NOCACHE) ]内存一次性装在几个,系统崩溃后出错
· NEXTVAL returns the next available sequence value.It returns a unique value everytime it is referenced, even for different users.
· CURRVAL obtains the current sequence value.
· NEXTVAL must be issued for that sequence before CURRVAL contains a value.
Insert a new department named“Support”in location ID 2500:
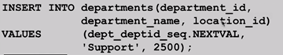
View the current value for the DEPT_DEPTID_SEQ sequence:

Caching Sequence Values
· Caching sequence values in memory gives faster access to those values.
· Gaps in sequence values can occur when:序列号断层
—A rollback occurs
—The system crashes
—A sequence is used in another table
Guidelines for Modifying a SequenceALTER SEQUENCE 序列名 [INCREMENT BY n] [START WITH n]不能修改初始值,必须先删除 [(MAXVALUE n | NOMAXVALUE)] [(MINVALUE n | NOMINVALUE)] [(CYCLE | NOCYCLE) ] [(CACHE n | NOCACHE) ]
· Only future sequence numbers are affected.
· The sequence must be dropped and re-created to restart the sequence at a different number.
· Some validation is performed.
· To remove a sequence, use the DROP statement:Index索引
· is a schema object
· Can be used by the Oracle server to speed up the retrieval of rows by using a pointer
· Can reduce disk input/output(I/O) by using a rapid path access method to locate data quickly
· is independent of the table that it indexes
· is used and maintained automatically by the oracle server
· 自动创建:主键或unique的字段
Automatically:A unique index is created automatically when you define a PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE constraint in a table definition.
· 手动创建Manually:Users can create nonunique indexes on columns to speed up access to the rows.create [unique][bitmap]index 索引名 on table表名(column字段,…)和表的字段对应 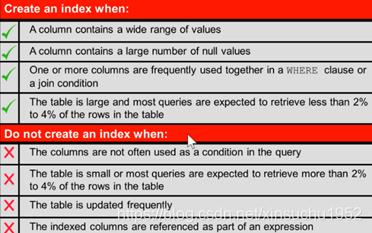
Drop index 索引名;删除 Synonym同义词
Simplify access to objects by creating a synonym(another name for an object) .With synonyms, you can:
· Create an easier reference to a table that is owned by another user
· Shorten lengthy object namesCREATE [PUBLIC] SYNONYM synonym FOR object; DROP SYNONYM 同义词;删除
本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)