目录 上一篇文章,我们讲了OpenCV的基本使用,前面的基本使用,也是我们以后每次课程几乎都会涉及到的。想要真正掌握,其实就一个办法:多练! 从这节课开始,我们进入OpenCV的核心模块,来了解OpenCV中最基础,最核心的东西。这节课将带领大家一起来了解OpenCV最基本的结构Mat类。接下来就跟我一起走进Mat的世界吧! 我们眼中的世界是什么样的呢? 我想,可能是这样: 可能是这样: 还可能是这样: 但是在计算机的眼中,这个世界是什么样的呢? 是这个样子的 到了计算机中都是一堆数字,这些数字就是图像的像素,上面这个图是一个灰度图像,数组代表像素值,0表示纯黑,255表示纯白,数字越大,颜色越浅。 上面我们了解到在计算机中,他们的世界就是一堆数字,那他们怎么存储呢?在OpenCV中,我们使用一个类Mat来存放图像,我们怎么理解容器呢? 大家已经学到这里,我想大家应该至少了解一门其他编程语言,大家都应该学过变量类型,变量类型可以用来声明一个变量。类也是如此,类是一组具有共同特征的物体的抽象表达。它有比变量更加丰富多样化的功能,类生成的实例我们称之为对象。类不仅有自己的数据,还有自己的方法。Mat类负责在OpenCV中声明一个图像类型的变量。用来存放图像数据。 在OpenCV中,Mat类的定义如下: 着实有点多,接下来我们把最常用的分类给大家详细讲解,让大家有个系统认识。 上面那个是整体,确实太多啦,所以在这里,给大家讲解一下常用的成员及方法。 第一个要说的就是常用成员,主要有如下几个: 接下来我们详细说一下: flags用于指定图像的颜色空间,flags有三个类型的取值: 如果flags>0,那么图像就是三通道的彩色图像; 如果flags=0,那么图像就是灰度图像; 如果flags<0,那么不做改变; 我们通过几个代码来看一下效果: 我们读取一张图像之后,显示一下图像,并查看该图像的flags: src.flags = 1124024336 如果我们将图像的flags设为0,那么图像变为: 大家也可以自己尝试一下如果设为其他正值,图像会是什么样子,我取值为1,得到的如下: 如果设为负值,就会报异常。 dims表示的是数据的维数,因为我们做的是二维图像,所以我们的维数是2,如果我们创建一个三维的数据,那我们得到的就是三维: 上面我们是获取一个二维图像,那我们得到的结果应该是2: 如果我们创建一个三维的数据,那我们看一下效果。在这里,我们要使用Mat的构造方法,不用担心,后面我们会讲到常用的构造方法: 上面我们是生成了一个三维图像,那我们得到的结果应该是3。 这两个就比较简单了,得到的是图像的行和列。而且大家不要记混了: rows是行,cols是列。 这样,我们每次加载一个图像,就能清楚知道它的尺寸啦!代码如下: 结果如下: uchar类型的指针,指向Mat数据矩阵的首地址。这个指的是图像数据,在输出过程中,如果我们想输出其对应的值,我们需要使用强制类型转换为int类型,代码如下:(为了方便查看输出结果,我们截取图像的某一部分) 结果如下: Mat有很多构造函数,下面是Mat定义中的构造函数和析构函数: 但其实我们一般能用到的并不多,主要有如下几类: 第一种类型就是尺寸 + 类型,尺寸有的通过一个参数定义,比如: 有的通过多个参数定义,比如: 类型定义如下: 所以这一类型主要有: 第二种类型在基本类型的基础上增加了颜色,也就是尺寸 + 类型 + 颜色, 其中表示颜色的是: 这一类型主要有: 第三种类型就是在基本类型中添加数据data,也就是尺寸 + 类型 + 数据, 其中表示数据的是: 这一类型主要有: 第四种类型就是在Mat类型加上其他参数,也就是Mat + 其他, 这一类型主要有: 这种类型中最常用的是第三个,也就是可以获取图像中某个矩形区域内的图像,例如: 我们的输入图像为: 使用Mat构造函数 Mat(const Mat& m, const Rect& roi); 后的图像为: 除了构造函数,Mat类还支持很多其他方法,在这里把一些常用的方法介绍给大家。 第一类是跟图像的行列相关,主要有: 第二种类型是通过一个图像拷贝到另一个图像,或者转换后拷贝到另一个图像,主要有: 第三种类型是基本运算,因为我们知道,二维图像其实就是二维矩阵,对二维图像的操作包括修改形状尺寸,图像矩阵求逆,两个图像矩阵相乘等等,主要有: 第四种类型是生成全一、全零、对角矩阵或者按类型生成矩阵,主要有: 第五种类型是获取图像基本信息,主要有: 当然Mat的函数不止有这些,其他的,如果大家深入学习,有可能会用到,在这里就不讲了。还是希望大家能够多多练习,多多尝试。 上面的主要是讲解,这里,我们通过几个实际的例子来使用一下,加深我们的印象。 这个是最简单的,也是最常用的,我们使用一个图像类型,就要使用Mat进行声明: 我们可以使用Mat类型来生成对象,上面我们讲了很多构造方法,大家可以逐一尝试,在这里,我们举几个例子: 这个时候,我们就涉及到两个概念:浅拷贝与深拷贝。 浅拷贝只复制指向某个对象的指针,而不复制对象本身,新旧对象还是共享同一块内存。修改某一个对象,另一个对象就会一同被修改。 深拷贝会另外创造一个一模一样的对象,新对象跟原对象不共享内存,修改新对象不会改到原对象。 下面的方式是浅拷贝方式: 使用copyTo函数和clone函数可以实现深拷贝,下面的方式是深拷贝方式: 简单使用就是说我们只考虑其类体中的方法,因为OpenCV的其他模块,都可以用Mat创建的对象调用,在后续课程我们会继续讲解。 我们可以访问常用成员获得图像的基本信息: 我们可以使用Mat的方法获得图像的基本信息: 执行结果如下: 我们可以生成全一全零或者单位矩阵: 执行结果如下: 根据我们上面讲的,我们总结一下在使用过程中的注意事项: 1.OpenCV中的内存分配是自动完成的(不是特别指定的话) 2.使用OpenCV的C++ 接口时不需要考虑内存释放问题 3.Mat的赋值运算和拷贝构造函数只会拷贝矩阵头,仍然共同同一个矩阵 4.如果要复制矩阵数据,可以使用clone和copyTo函数 讲到这里,Mat就基本讲的差不多了,在最后,给大家来点科普,其实在最开始,OpenCV使用的图像类型不是Mat,而是另外两个,那为什么要引入Mat呢? 1.语言的变化,OpenCV1.x版本使用C语言编写,从2.x版本引入C++之后,换用C++来写。 2.单从上面一条肯定是不行,主要还是因为这一条:C++提供了很多新特性,比如类可以在结束时自动调用析构函数,释放内存,就不需要再自己写代码释放了,但是C语言不行,申请的内存需要自己手动管理,特别是采用 lplImage 会直接暴露内存,如果忘记释放内存,就会造成内存泄漏。而Mat的内存分配和释放,由Mat类自己管理。 3.Mat相对于前两个功能更加强大,Mat既可以深拷贝也可以浅拷贝,Mat在进行浅拷贝时,只复制矩阵头,而不复制矩阵,提高效率。如果矩阵属于多个Mat对象,则通过引用计数来判断,当最后一个使用它的对象,则负责释放矩阵。 所以上面的也是Mat的优势。 但是在很多时候,很多人还是会使用另外两个,那我们就要考虑他们的类型转换了,这里我将类型转换方式给大家:
一、前言
二、Mat定义
1、你眼中的世界VS电脑眼中的世界




2、Mat是个啥
3、Mat代码定义
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: Mat(); Mat(int rows, int cols, int type); Mat(Size size, int type); Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, const Scalar& s); Mat(Size size, int type, const Scalar& s); Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type); Mat(const std::vector<int>& sizes, int type); Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, const Scalar& s); Mat(const std::vector<int>& sizes, int type, const Scalar& s); Mat(const Mat& m); Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, void* data, size_t step=AUTO_STEP); Mat(Size size, int type, void* data, size_t step=AUTO_STEP); Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, void* data, const size_t* steps=0); Mat(const std::vector<int>& sizes, int type, void* data, const size_t* steps=0); Mat(const Mat& m, const Range& rowRange, const Range& colRange=Range::all()); Mat(const Mat& m, const Rect& roi); Mat(const Mat& m, const Range* ranges); Mat(const Mat& m, const std::vector<Range>& ranges); template<typename _Tp> explicit Mat(const std::vector<_Tp>& vec, bool copyData=false); template<typename _Tp, typename = typename std::enable_if<std::is_arithmetic<_Tp>::value>::type> explicit Mat(const std::initializer_list<_Tp> list); template<typename _Tp> explicit Mat(const std::initializer_list<int> sizes, const std::initializer_list<_Tp> list); template<typename _Tp, size_t _Nm> explicit Mat(const std::array<_Tp, _Nm>& arr, bool copyData=false); template<typename _Tp, int n> explicit Mat(const Vec<_Tp, n>& vec, bool copyData=true); template<typename _Tp, int m, int n> explicit Mat(const Matx<_Tp, m, n>& mtx, bool copyData=true); template<typename _Tp> explicit Mat(const Point_<_Tp>& pt, bool copyData=true); template<typename _Tp> explicit Mat(const Point3_<_Tp>& pt, bool copyData=true); template<typename _Tp> explicit Mat(const MatCommaInitializer_<_Tp>& commaInitializer); //! download data from GpuMat explicit Mat(const cuda::GpuMat& m); //! destructor - calls release() ~Mat(); Mat& operator = (const Mat& m); Mat& operator = (const MatExpr& expr); //! retrieve UMat from Mat UMat getUMat(AccessFlag accessFlags, UMatUsageFlags usageFlags = USAGE_DEFAULT) const; Mat row(int y) const; Mat col(int x) const; Mat rowRange(int startrow, int endrow) const; Mat rowRange(const Range& r) const; Mat colRange(int startcol, int endcol) const; Mat colRange(const Range& r) const; Mat diag(int d=0) const; static Mat diag(const Mat& d); Mat clone() const CV_NODISCARD; void copyTo( OutputArray m ) const; void copyTo( OutputArray m, InputArray mask ) const; void convertTo( OutputArray m, int rtype, double alpha=1, double beta=0 ) const; void assignTo( Mat& m, int type=-1 ) const; Mat& operator = (const Scalar& s); Mat& setTo(InputArray value, InputArray mask=noArray()); Mat reshape(int cn, int rows=0) const; /** @overload */ Mat reshape(int cn, int newndims, const int* newsz) const; /** @overload */ Mat reshape(int cn, const std::vector<int>& newshape) const; MatExpr t() const; MatExpr inv(int method=DECOMP_LU) const; MatExpr mul(InputArray m, double scale=1) const; Mat cross(InputArray m) const; double dot(InputArray m) const; static MatExpr zeros(int rows, int cols, int type); static MatExpr zeros(Size size, int type); static MatExpr zeros(int ndims, const int* sz, int type); static MatExpr ones(int rows, int cols, int type); static MatExpr ones(Size size, int type); static MatExpr ones(int ndims, const int* sz, int type); static MatExpr eye(int rows, int cols, int type); static MatExpr eye(Size size, int type); void create(int rows, int cols, int type); void create(Size size, int type); void create(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type); void create(const std::vector<int>& sizes, int type); void addref(); void release(); //! internal use function, consider to use 'release' method instead; deallocates the matrix data void deallocate(); //! internal use function; properly re-allocates _size, _step arrays void copySize(const Mat& m); void reserve(size_t sz); void reserveBuffer(size_t sz); void resize(size_t sz); void resize(size_t sz, const Scalar& s); //! internal function void push_back_(const void* elem); template<typename _Tp> void push_back(const _Tp& elem); template<typename _Tp> void push_back(const Mat_<_Tp>& elem); template<typename _Tp> void push_back(const std::vector<_Tp>& elem); void push_back(const Mat& m); void pop_back(size_t nelems=1); void locateROI( Size& wholeSize, Point& ofs ) const; Mat& adjustROI( int dtop, int dbottom, int dleft, int dright ); Mat operator()( Range rowRange, Range colRange ) const; Mat operator()( const Rect& roi ) const; Mat operator()( const Range* ranges ) const; Mat operator()(const std::vector<Range>& ranges) const; template<typename _Tp> operator std::vector<_Tp>() const; template<typename _Tp, int n> operator Vec<_Tp, n>() const; template<typename _Tp, int m, int n> operator Matx<_Tp, m, n>() const; template<typename _Tp, std::size_t _Nm> operator std::array<_Tp, _Nm>() const; bool isContinuous() const; //! returns true if the matrix is a submatrix of another matrix bool isSubmatrix() const; size_t elemSize() const; size_t elemSize1() const; int type() const; int depth() const; int channels() const; size_t step1(int i=0) const; bool empty() const; size_t total() const; size_t total(int startDim, int endDim=INT_MAX) const; int checkVector(int elemChannels, int depth=-1, bool requireContinuous=true) const; uchar* ptr(int i0=0); /** @overload */ const uchar* ptr(int i0=0) const; uchar* ptr(int row, int col); const uchar* ptr(int row, int col) const; /** @overload */ uchar* ptr(int i0, int i1, int i2); /** @overload */ const uchar* ptr(int i0, int i1, int i2) const; /** @overload */ uchar* ptr(const int* idx); /** @overload */ const uchar* ptr(const int* idx) const; /** @overload */ template<int n> uchar* ptr(const Vec<int, n>& idx); /** @overload */ template<int n> const uchar* ptr(const Vec<int, n>& idx) const; /** @overload */ template<typename _Tp> _Tp* ptr(int i0=0); /** @overload */ template<typename _Tp> const _Tp* ptr(int i0=0) const; template<typename _Tp> _Tp* ptr(int row, int col); template<typename _Tp> const _Tp* ptr(int row, int col) const; /** @overload */ template<typename _Tp> _Tp* ptr(int i0, int i1, int i2); /** @overload */ template<typename _Tp> const _Tp* ptr(int i0, int i1, int i2) const; /** @overload */ template<typename _Tp> _Tp* ptr(const int* idx); /** @overload */ template<typename _Tp> const _Tp* ptr(const int* idx) const; /** @overload */ template<typename _Tp, int n> _Tp* ptr(const Vec<int, n>& idx); /** @overload */ template<typename _Tp, int n> const _Tp* ptr(const Vec<int, n>& idx) const; template<typename _Tp> _Tp& at(int i0=0); template<typename _Tp> const _Tp& at(int i0=0) const; template<typename _Tp> _Tp& at(int row, int col); template<typename _Tp> const _Tp& at(int row, int col) const; template<typename _Tp> _Tp& at(int i0, int i1, int i2); template<typename _Tp> const _Tp& at(int i0, int i1, int i2) const; template<typename _Tp> _Tp& at(const int* idx); template<typename _Tp> const _Tp& at(const int* idx) const; /** @overload */ template<typename _Tp, int n> _Tp& at(const Vec<int, n>& idx); /** @overload */ template<typename _Tp, int n> const _Tp& at(const Vec<int, n>& idx) const; template<typename _Tp> _Tp& at(Point pt); template<typename _Tp> const _Tp& at(Point pt) const; template<typename _Tp> MatIterator_<_Tp> begin(); template<typename _Tp> MatConstIterator_<_Tp> begin() const; template<typename _Tp> MatIterator_<_Tp> end(); template<typename _Tp> MatConstIterator_<_Tp> end() const; template<typename _Tp, typename Functor> void forEach(const Functor& operation); /** @overload */ template<typename _Tp, typename Functor> void forEach(const Functor& operation) const; Mat(Mat&& m); Mat& operator = (Mat&& m); enum { MAGIC_VAL = 0x42FF0000, AUTO_STEP = 0, CONTINUOUS_FLAG = CV_MAT_CONT_FLAG, SUBMATRIX_FLAG = CV_SUBMAT_FLAG }; enum { MAGIC_MASK = 0xFFFF0000, TYPE_MASK = 0x00000FFF, DEPTH_MASK = 7 }; int flags; //! the matrix dimensionality, >= 2 int dims; //! the number of rows and columns or (-1, -1) when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions int rows, cols; //! pointer to the data uchar* data; //! helper fields used in locateROI and adjustROI const uchar* datastart; const uchar* dataend; const uchar* datalimit; //! custom allocator MatAllocator* allocator; //! and the standard allocator static MatAllocator* getStdAllocator(); static MatAllocator* getDefaultAllocator(); static void setDefaultAllocator(MatAllocator* allocator); //! internal use method: updates the continuity flag void updateContinuityFlag(); //! interaction with UMat UMatData* u; MatSize size; MatStep step; protected: template<typename _Tp, typename Functor> void forEach_impl(const Functor& operation); }; 三、常用成员及方法介绍
1、常用成员
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: /*flags指定图像的颜色空间 flags > 0 3通道的彩色图像 flags = 0 灰度图像 flags < 0 不作改变 */ int flags; /*数据的维数*/ int dims; /*行和列的数量;数组超过2维时为(-1,-1)*/ int rows, cols; uchar* data; // 图像数据 }; 1.flags
Mat src; src = imread("./image/cat.jpg"); imshow("src", src); cout << "src.flags = " << src.flags << endl; src.flags = 0; imshow("src.flags = 0", src);

2.dims
Mat src; src = imread("./image/cat.jpg"); cout << "src.flags = " << src.flags << endl; cout << "src.dims = " << src.dims << endl;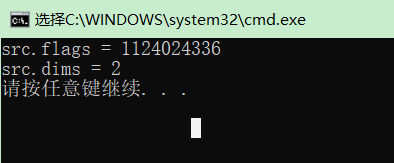
Mat src; src = imread("./image/cat.jpg"); cout << "src.flags = " << src.flags << endl; cout << "src.dims = " << src.dims << endl;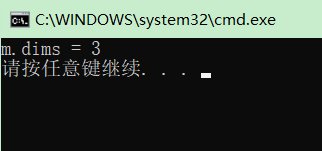
3.rows&cols
Mat src; src = imread("./image/cat.jpg"); cout << "src.rows = " << src.rows << endl; cout << "src.cols = " << src.cols << endl;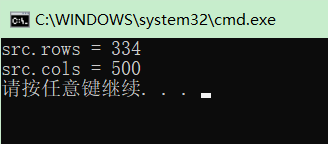
4.data
Mat src; src = imread("./image/cat.jpg"); if (!src.data) { cout << "ERROR : could not load image.n"; waitKey(0); return -1; } src = Mat(src, Rect(280, 100, 20, 20)); cout << "src.rows = " << src.rows << endl; cout << "src.cols = " << src.cols << endl; cout << "src.data = " << endl; for (int i = 0; i < src.cols*src.rows; i++) { cout << (int)src.data[i] << " "; if (i%src.rows == src.rows - 1) cout << endl; }
2、构造函数
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: Mat(); Mat(int rows, int cols, int type); Mat(Size size, int type); Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, const Scalar& s); Mat(Size size, int type, const Scalar& s); Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type); Mat(const std::vector<int>& sizes, int type); Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, const Scalar& s); Mat(const std::vector<int>& sizes, int type, const Scalar& s); Mat(const Mat& m); Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, void* data, size_t step=AUTO_STEP); Mat(Size size, int type, void* data, size_t step=AUTO_STEP); Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, void* data, const size_t* steps=0); Mat(const std::vector<int>& sizes, int type, void* data, const size_t* steps=0); Mat(const Mat& m, const Range& rowRange, const Range& colRange=Range::all()); Mat(const Mat& m, const Rect& roi); Mat(const Mat& m, const Range* ranges); Mat(const Mat& m, const std::vector<Range>& ranges); template<typename _Tp> explicit Mat(const std::vector<_Tp>& vec, bool copyData=false); template<typename _Tp, typename = typename std::enable_if<std::is_arithmetic<_Tp>::value>::type> explicit Mat(const std::initializer_list<_Tp> list); template<typename _Tp> explicit Mat(const std::initializer_list<int> sizes, const std::initializer_list<_Tp> list); template<typename _Tp, size_t _Nm> explicit Mat(const std::array<_Tp, _Nm>& arr, bool copyData=false); template<typename _Tp, int n> explicit Mat(const Vec<_Tp, n>& vec, bool copyData=true); template<typename _Tp, int m, int n> explicit Mat(const Matx<_Tp, m, n>& mtx, bool copyData=true); template<typename _Tp> explicit Mat(const Point_<_Tp>& pt, bool copyData=true); template<typename _Tp> explicit Mat(const Point3_<_Tp>& pt, bool copyData=true); template<typename _Tp> explicit Mat(const MatCommaInitializer_<_Tp>& commaInitializer); //! download data from GpuMat explicit Mat(const cuda::GpuMat& m); //! destructor - calls release() ~Mat(); }; 1.基本:尺寸 + 类型
Mat(Size size, int type);
Mat(int rows, int cols, int type);
int type;
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: Mat(int rows, int cols, int type); Mat(Size size, int type); Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type); Mat(const std::vector<int>& sizes, int type); }; 2.基本 + 颜色
const Scalar& s;
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, const Scalar& s); Mat(Size size, int type, const Scalar& s); Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, const Scalar& s); Mat(const std::vector<int>& sizes, int type, const Scalar& s); }; 3.基本+数据
void* data;
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, void* data, size_t step=AUTO_STEP); Mat(Size size, int type, void* data, size_t step=AUTO_STEP); Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, void* data, const size_t* steps=0); Mat(const std::vector<int>& sizes, int type, void* data, const size_t* steps=0); }; 4.Mat+其他
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: Mat(const Mat& m); Mat(const Mat& m, const Range& rowRange, const Range& colRange=Range::all()); Mat(const Mat& m, const Rect& roi); Mat(const Mat& m, const Range* ranges); Mat(const Mat& m, const std::vector<Range>& ranges); };
Mat src, src_roi; src = imread("./image/cat.jpg"); if (!src.data) { cout << "ERROR : could not load image.n"; waitKey(0); return -1; } imshow("input image", src); src_roi = Mat(src, Rect(100, 100, 300, 200)); imshow("roi image", src_roi);

3、其他方法
1.行与列
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: Mat row(int y) const; Mat col(int x) const; Mat rowRange(int startrow, int endrow) const; Mat rowRange(const Range& r) const; Mat colRange(int startcol, int endcol) const; Mat colRange(const Range& r) const; }; 2.拷贝与转换
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: Mat clone() const CV_NODISCARD; void copyTo( OutputArray m ) const; void copyTo( OutputArray m, InputArray mask ) const; void convertTo( OutputArray m, int rtype, double alpha=1, double beta=0 ) const; void assignTo( Mat& m, int type=-1 ) const; Mat& setTo(InputArray value, InputArray mask=noArray()); }; 3.基本运算
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: Mat reshape(int cn, int rows=0) const; Mat reshape(int cn, int newndims, const int* newsz) const; Mat reshape(int cn, const std::vector<int>& newshape) const; MatExpr inv(int method=DECOMP_LU) const; MatExpr mul(InputArray m, double scale=1) const; Mat cross(InputArray m) const; double dot(InputArray m) const; void resize(size_t sz); void resize(size_t sz, const Scalar& s); }; 4.生成图像矩阵
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: static MatExpr zeros(int rows, int cols, int type); static MatExpr zeros(Size size, int type); static MatExpr zeros(int ndims, const int* sz, int type); static MatExpr ones(int rows, int cols, int type); static MatExpr ones(Size size, int type); static MatExpr ones(int ndims, const int* sz, int type); static MatExpr eye(int rows, int cols, int type); static MatExpr eye(Size size, int type); void create(int rows, int cols, int type); void create(Size size, int type); void create(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type); void create(const std::vector<int>& sizes, int type); }; 5.图像基本信息
class CV_EXPORTS Mat { public: int type() const; //类型 int depth() const; //图像深度 int channels() const; //图像通道数 bool empty() const; //图像是否为空 }; 四、Mat使用
1、Mat创建对象
1.声明对象
Mat src;2.构造函数生成对象
Mat src_rect, src_type, src_color; src_rect = Mat(src, Rect(100, 100, 300, 200)); src_type = Mat(10, 10, CV_8UC1); src_color = Mat(10, 10,CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0, 255));3.拷贝生成对象
Mat light_copy_1(src); Mat light_copy_2 = src;
Mat deep_copy_1 = src.clone(); Mat deep_copy_2; src.copyTo(deep_copy_2);2、Mat对象的简单使用
cout << "src.flags = " << src.flags << endl; cout << "src.dims = " << src.dims << endl; cout << "src.rows = " << src.rows << endl; cout << "src.cols = " << src.cols << endl; cout << "src.data = " << endl; for (int i = 0; i < src.cols*src.rows; i++) { cout << (int)src.data[i] << " "; if (i%src.rows == src.rows - 1) cout << endl; }
Mat src; src = imread("./image/cat.jpg"); if (src.empty()) { cout << "ERROR : could not load image.n"; return -1; } cout << "src.channels() = " << src.channels() << endl; cout << "src.type() = " << src.type() << endl; cout << "src.depth() = " << src.depth() << endl;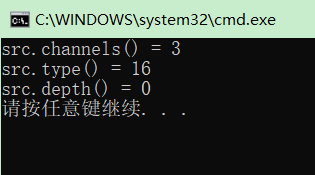
Mat E = Mat::eye(4, 4, CV_64F); cout << "E = " << endl << E << endl << endl; Mat O = Mat::ones(2, 2, CV_32F); cout << "O = " << endl << O << endl << endl; Mat Z = Mat::zeros(3, 3, CV_8UC1); cout << "Z = " << endl << Z << endl << endl;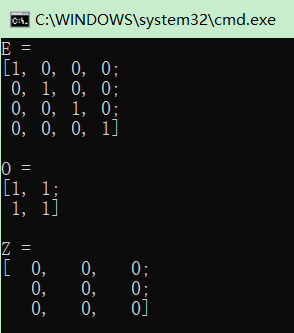
3、Mat注意事项
五、Mat与CVMat,IplImage
1、为何引入Mat
2、类型转换
//1. IpIImage -> CvMat /*cvGetMat*/ CvMat matheader; CvMat * mat = cvGetMat(img, &matheader); /*cvConvert*/ CvMat * mat = cvCreateMat(img->height, img->width, CV_64FC3); cvConvert(img, mat); //2. IplImage -> Mat Mat::Mat(const IplImage* img, bool copyData=false);/*default copyData=false,与原来的IplImage共享数据,只是创建一个矩阵头*/ //例子: IplImage* iplImg = cvLoadImage("greatwave.jpg", 1); Mat mtx(iplImg); /* IplImage * -> Mat,共享数据; or : Mat mtx = iplImg;*/ //3. Mat -> IplImage Mat M IplImage iplimage = M; /*只创建图像头,不复制数据*/ //4. CvMat -> Mat Mat::Mat(const CvMat* m, bool copyData=false); /*类似IplImage -> Mat,可选择是否复制数据*/ //5. Mat -> CvMat //例子(假设Mat类型的imgMat图像数据存在): CvMat cvMat = imgMat;/*Mat -> CvMat, 类似转换到IplImage,不复制数据只创建矩阵头
本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)