前面一篇文章Android进阶——Material Design新控件之利用CoordinatorLayout协同多控件交互(七)介绍了下CoordinatorLayout 的简单应用,在使用的时候,你是否有想过为何CoordinatorLayout比其他ViewGroup具有可以让直接子View交互的功能?相关系列文章链接如下: CoordinatorLayout直接继承自ViewGroup并且实现了NestedScrollingParent2接口,核心参与角色主要有:CoordinatorLayout.CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams、CoordinatorLayout.Behavior两个内部类。 NestedScrollingParent2接口主要是用于处理嵌套滑动事件的,本质上也没有什么特别的逻辑,和Behavior一样是预约定好的接口API,区别在于Behavior是由CoordinatorLayout赋能,而NestedScrollingParent2是由实现此接口的View进行赋能。 CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams是CoordinatorLayout的内部类,和其他ViewGroup功能类似,在CoordinatorLayout的generateLayoutParams方法中直接调用构造方法进行初始化且在CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams构造方法内部调用CoordinatorLayout的parseBehavior根据配置的Behavior的类名反射创建Behavior并赋值到mBehavior字段,然后再通过Behavior的onAttachedToLayoutParams方法Called when the Behavior has been attached to a LayoutParams instance.,所以除了保存CoordinatorLayout内的子控件的布局信息之外,还保存着对应的Behavior对象引用 mBehavior。 这个类设计的原因是在于我们要在XML中通过自定义的属性给主题View绑定对应的Behavior,所以需要重写generateLayoutParams方法传入自定义的属性。 CoordinatorLayout.Behavior是CoordinatorLayout的抽象泛型内部类,Behvaior 本身并不具备具体的业务功能,本质上就只是为了进行解耦的而封装的一个交互接口集合类,而CoordinatorLayout可以借助Behavior使得独立的子View可以产生交互,是因为CoordinatorLayout内部把事件分发至Behavior,让Behavior具有可以控制其他子View的效果了,也是CoordinatorLayout中核心的设计,也正是因为这个CoordinatorLayout.Behavior使得CoordinatorLayout中的直接子控件间可以产生联系,CoordinatorLayout.Behavior可以理解为事件分发的传送渠道(并不负责具体的任务),只是负责调用对应子View的相关方法,parseBehavior方法根据配置的Behavior的类名反射创建Behavior并赋值到mBehavior字段,这是继承Behavior时必须要重写两个参数的构造方法的原因。通俗来说,Behavior 设置在谁身上,就可以通过Behavior来改变它对应的状态,观察者改变时,主题也跟着改变。 CoordinatorLayout.Behavior中最核心的方法只有三个:layoutDependsOn方法、onDependentViewChanged方法和onDependentViewRemoved方法,通过这三个方法就可以实现直接子View之间的交互,至于其他方法是处理到其他业务情况的时候,比如说嵌套滑动、重新布局等等。 当进行Layout请求的时候就会触发执行,给CoordinatorLayout中的直接子控件设置了对应的Behavior之后,绘制时至少会执行一次,表示是否给配置了Behavior 的CoordinatorLayout直接子View 指定一个作为观察者角色的子View,返回true则表示主题角色child view的观察者是dependency view, 当观察者角色View状态(大小、位置)发生变化时,不管被观察View 的顺序怎样,被观察的View也可监听到并回调对应的方法;反之则两者之间没有建立联系。简而言之,这个方法的作用是配置了Behavior的主题子控件被符合哪些条件逻辑的子控件观察的(即作为主题的观察者之一)(Determine whether the supplied child view has another specific sibling view as a layout dependency)。 当且仅当Dependency View 状态(位置、大小等)改变时就会触发,返回true则表示Behavior改变了主题的状态,可能会执行多次,当然第一次绘制到布局上也算是状态改变时,所以自然也会触发,至于当监听到改变之后,如何去实现什么样的效果则由我们自己去开发实现。 当依赖的Dependency View被移除时触发回调(Respond to a child’s dependent view being removed.) 设置是否拦截触摸事件,返回true则表示当前Behavior会拦截触摸事件,不会分发到CoordinatorLayout内的子View下了。 xxNestedxxScrollxx方法是用于监听嵌套滑动的事件,对应的是NestedScrollingParent2接口里的相关方法。 当CoordinatorLayout 的子View试图开始进行嵌套滑动的时候触发,返回true时表示CoordinatorLayout充当nested scroll parent 处理这次滑动,当且仅当返回true时,当前Behavior才能收到后面的一些nested scroll事件回调(如:onNestedPreScroll、onNestedScroll等)。 在嵌套滑动进行中且onStartNestedScroll方法返回true时回调,当子View调用dispatchNestedPreScroll方法时会调用该方法。 onStartNestedScroll方法返回true且嵌套滑动进行前,要监听的子 View将要滑动,滑动事件即将被消费(但最终被谁消费,可以通过代码控制) 用户松开手指后会进行惯性滑动时调用,参数提供了速度信息,可以根据这些速度信息决定最终状态。 用户松开手指后会发生惯性动作之前调用,参数提供了速度信息,可以根据这些速度信息决定最终状态,比如滚动Header,是让Header处于展开状态还是折叠状态,返回true 则表示消费了fling. 在嵌套滑动结束(ACTION_UP或ACTION_CANCEL)时触发。 简单来说,抛开CoordinatorLayout 这个Behavior里的所有方法都没有任务具体的功能,是CoordinatorLayout为了解耦,抽象了一层接口并封装为Behavior,当CoordinatorLayout里进行事件分发时主动去调用Behavior的接口即赋能。 Behavior机制适用于同一Parent ViewGroup下相互独立的子View之间进行交互,如果View之间已经存在引用联系则没有必要去使用Behavior增加复杂度了。 CoordinatorLayout本质上就是ViewGroup+Behavior 模型搭建为变形的“观察者模式”,观察者View和主题View都隶属于CoordinatorLayout直接子View,通过在布局中给控件配置app:layout_behavior属性来指定主题角色,再在这个Behavior 中的layoutDependsOn方法给主题寻找对应的观察者角色,这样就建立了联系,当观察者的位置、大小等状态改变时,主题也可监听到并回调Behavior里的方法。 generateLayoutParams方法的作用是定义父View下所有子View所使用的LayoutParams类,只要重写了generateLayoutParams方法,所有子View就一定会使用重写的LayoutParams来修饰自己,比如说你自定ViewGroup时需要把自定义的属性传入,就需要重写这个方法。 Android事件分发主要是通过dispatchTouchEvent、onInterceptTouchEvent、onTouchEvent三个方法协同完成的,而CoordinatorLayout中没有重写dispatchTouchEvent方法说明使用的是其父类的逻辑并不是CoordinatorLayout所特有的,我们就把CoordinatorLayout的onInterceptTouchEvent方法当成事件分发的起点开始分析,当接收到DOWN或者UP或CANCEL事件时,遍历子View查找对应的Behavior并调用其对应的onInterceptTouchEvent或onTouchEvent方法并把返回值设置到CoordinatorLayout的onInterceptTouchEvent方法的返回值。 resetTouchBehaviors方法核心作用是触发Behavior中onInterceptTouchEvent或者onTouchEvent方法。 performIntercept方法核心作用是遍历子View找出对应的Behavior并得到onInterceptTouchEvent或onTouchEvent返回值,最后赋值到CoordinatorLayout的onInterceptTouchEvent中,相当于是给Behavior的onInterceptTouchEvent或onTouchEvent方法赋能,拦截或者不拦截事件。 然后,接着CoordinatorLayout的onTouchEvent方法被执行,如果不满足条件则继续往下分发,满足条件则调用主题View中的Behavior。 onMeasure方法遍历查找子View,只是遍历了直接子View没有进行递归操作,所以这也是为什么仅支持直接子View去交互的原因。 prepareChildren方法添加子View时,获取对应的Behavior并执行layoutDependsOn方法 CoordinatorLayout的dependsOn方法真正去调用Behavior的layoutDependsOn方法。 当CoordinatorLayout的子View位置改变时,会主动触发onChildViewsChanged方法,最终实现通过调用Behavior的onDependentViewChanged方法通知,其他Behavior方法赋能方式也类似。 CoordinatorLayout负责监听子View之间状态变化并及时通知Behavior,使得监听和监听之后的处理解耦,CoordinatorLayout只负责告知你观察者改变了,你主题View想要做何改变,就在Behavior对应的方法实现,以上就是CoordinatorLayout核心流程,仅供参考。 源码版本Android 28
文章大纲
引言
一、CoordinatorLayout核心角色
1、CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams
public class CoordinatorLayout extends ViewGroup implements NestedScrollingParent2 { ... public static class LayoutParams extends MarginLayoutParams { ... Behavior mBehavior; LayoutParams(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout); this.gravity = a.getInteger(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_android_layout_gravity,Gravity.NO_GRAVITY); mAnchorId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_anchor,View.NO_ID); this.anchorGravity = a.getInteger(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_anchorGravity,Gravity.NO_GRAVITY); this.keyline = a.getInteger(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_keyline,-1); insetEdge = a.getInt(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_insetEdge, 0); dodgeInsetEdges = a.getInt(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_dodgeInsetEdges, 0); mBehaviorResolved = a.hasValue(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_behavior); if (mBehaviorResolved) { mBehavior = parseBehavior(context, attrs, a.getString(R.styleable.CoordinatorLayout_Layout_layout_behavior)); } a.recycle(); if (mBehavior != null) { // If we have a Behavior, dispatch that it has been attached mBehavior.onAttachedToLayoutParams(this); } } } ... } 2、CoordinatorLayout.Behavior
2、CoordinatorLayout.Behavior核心方法
2.1、layoutDependsOn方法
@Override public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent, View child, View dependency) { //TODO 在这里自己去实现依赖联系成立的逻辑,允许建立则返回true,完全不依赖CoordinatorLayout,实现解耦 if(dependency instanceof Button){ return true; } return super.layoutDependsOn(parent, child, dependency); } 2.2、onDependentViewChanged方法
/** * 当被观察者的View 状态(如:位置、大小)发生变化时就会触发执行 * @return true if the Behavior changed the child view's size or position, false otherwise */ @Override public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, View child, View dependency) { //TODO 根据具体的业务需求定义我们的结果 return super.onDependentViewChanged(parent, child, dependency); } 2.3、onDependentViewRemoved方法
/** * Respond to a child's dependent view being removed. * @param parent the parent view of the given child * @param child the child view to manipulate * @param dependency the dependent view that has been removed */ public void onDependentViewRemoved(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View dependency) { } 2.4、onInterceptTouchEvent方法设置是否拦截触摸事件
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, @NonNull MotionEvent ev) { return false; } 2.5、onTouchEvent方法处理触摸事件
public boolean onTouchEvent(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, @NonNull MotionEvent ev) { return false; } 2.6、onMeasureChild方法测量使用Behavior的View尺寸
/** * Called when the parent CoordinatorLayout is about to measure the given child view. * @param child the child to measure * @return true if the Behavior measured the child view, false if the CoordinatorLayout * should perform its default measurement */ public boolean onMeasureChild(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed, int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) { return false; } 2.7、onLayoutChild方法重新布局使用Behavior的View
/** * Called when the parent CoordinatorLayout is about the lay out the given child view. * @return true if the Behavior performed layout of the child view, false to request default layout behavior */ public boolean onLayoutChild(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout parent, @NonNull V child, int layoutDirection) { return false; } 2.8、onStartNestedScroll方法
/** * @param coordinatorLayout 和Behavior 绑定的View的父CoordinatorLayout * @param child 和Behavior 绑定的View 观察者 * @param directTargetChild * @param target * @param nestedScrollAxes 嵌套滑动滑动方向 * @param type the type of input which cause this scroll event * @return true if the Behavior wishes to accept this nested scroll */ @Override public boolean onStartNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, View child, View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes, int type) { return super.onStartNestedScroll(coordinatorLayout, child, directTargetChild, target, nestedScrollAxes,type); } 2.9、onNestedScroll方法
/** * 进行嵌套滚动时被调用 * @param coordinatorLayout * @param child * @param target * @param dxConsumed target 已经消费的x方向的距离 * @param dyConsumed target 已经消费的y方向的距离 * @param dxUnconsumed x 方向剩下的滚动距离 * @param dyUnconsumed y 方向剩下的滚动距离即未消费的距离 */ @Override public void onNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, View child, View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, int type) { super.onNestedScroll(coordinatorLayout, child, target, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed,type); } 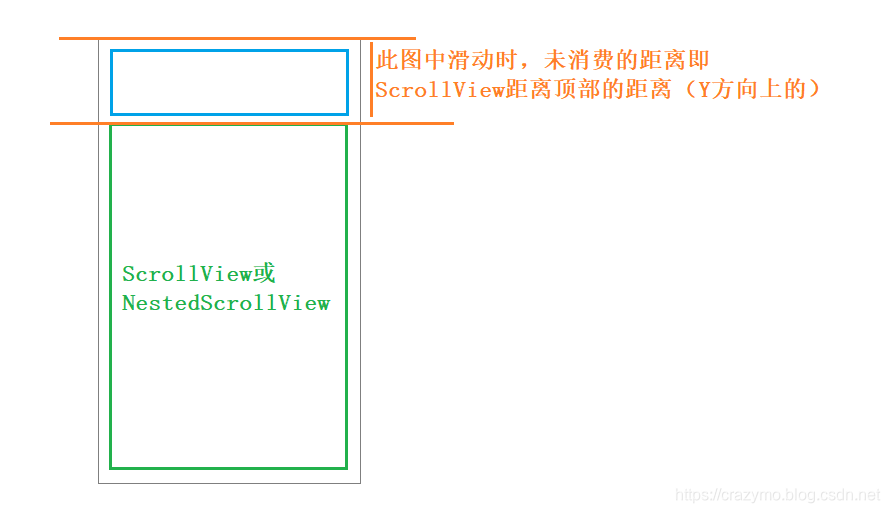
2.10、onNestedPreScroll方法
/** * 嵌套滚动发生之前被调用,nested scroll child 消费掉自己的滚动距离之前,嵌套滚动每次被nested scroll child * 更新都会调用onNestedPreScroll。 * @param coordinatorLayout * @param child * @param target * @param dx 用户水平方向的滚动距离 * @param dy 用户竖直方向的滚动距离 * @param consumed 可以修改这个数组表示你消费了多少距离,假设用户滑动了100px,child 做了90px 的位移,你需要把 consumed[1]的值改成90,这样CoordinatorLayout就能知道只处理剩下的10px的滚动。 */ @Override public void onNestedPreScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, View child, View target, int dx, int dy, int[] consumed, int type) { super.onNestedPreScroll(coordinatorLayout, child, target, dx, dy, consumed,type); } 2.11、onNestedFling方法
/** * Called when a nested scrolling child is starting a fling or an action that would * be a fling. * @param velocityX horizontal velocity of the attempted fling * @param velocityY vertical velocity of the attempted fling * @param consumed true if the nested child view consumed the fling * @return true if the Behavior consumed the fling * * @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedFling(View, float, float, boolean) */ public boolean onNestedFling(@NonNull CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, @NonNull V child, @NonNull View target, float velocityX, float velocityY, boolean consumed) { return false; } 2.12、onNestedPreFling方法
/** * * * @param coordinatorLayout * @param child * @param target * @param velocityX x 方向的速度 * @param velocityY y 方向的速度 * @return */ @Override public boolean onNestedPreFling(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, View child, View target, float velocityX, float velocityY) { return super.onNestedPreFling(coordinatorLayout, child, target, velocityX, velocityY); } 2.13、onStopNestedScroll方法
/** * 嵌套滚动结束时被调用,这是一个清除滚动状态等的好时机。 * @param coordinatorLayout * @param child * @param target */ @Override public void onStopNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, View child, View target, int type) { super.onStopNestedScroll(coordinatorLayout, child, target,type); } 二、CoordinatorLayout的核心流程解析
1、在CoordinatorLayout的generateLayoutParams方法中完成CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams的实例化
@Override public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) { return new LayoutParams(getContext(), attrs); } 2、在CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams构造方法中parseBehavior解析AttributeSet得到Behavior对应的类名
static final Class<?>[] CONSTRUCTOR_PARAMS = new Class<?>[] { Context.class, AttributeSet.class }; static Behavior parseBehavior(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, String name) { if (TextUtils.isEmpty(name)) { return null; } final String fullName; if (name.startsWith(".")) { fullName = context.getPackageName() + name; } else if (name.indexOf('.') >= 0) { fullName = name; } else { fullName = !TextUtils.isEmpty(WIDGET_PACKAGE_NAME)? (WIDGET_PACKAGE_NAME + '.' + name): name; } try { Map<String, Constructor<Behavior>> constructors = sConstructors.get(); if (constructors == null) { constructors = new HashMap<>(); sConstructors.set(constructors); } Constructor<Behavior> c = constructors.get(fullName); if (c == null) { final Class<Behavior> clazz = (Class<Behavior>) context.getClassLoader().loadClass(fullName); ///这是继承Behavior时必须要重写两个参数的构造方法的原因 c = clazz.getConstructor(CONSTRUCTOR_PARAMS); c.setAccessible(true); ///把构造方法缓存起来 constructors.put(fullName, c); } return c.newInstance(context, attrs); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException("Could not inflate Behavior subclass " + fullName, e); } } 3、CoordinatorLayout 处理事件分发时给Behavior对应的方法赋能
@Override public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { final int action = ev.getActionMasked(); // Make sure we reset in case we had missed a previous important event. if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) { //接收到DOWN事件时,遍历调用Behavior的调用onInterceptTouchEvent方法后回收事件,重置设置为false即让关联的Behavior可以与子View交互,true则阻止先前的交互 resetTouchBehaviors(true); } //判断是否拦截,到这一步才赋予Behavior里的onInterceptTouchEvent真正的拦截能力 final boolean intercepted = performIntercept(ev, TYPE_ON_INTERCEPT); if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP || action == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL) { resetTouchBehaviors(true); } return intercepted; } private void resetTouchBehaviors(boolean notifyOnInterceptTouchEvent) { final int childCount = getChildCount(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { final View child = getChildAt(i); final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); final Behavior b = lp.getBehavior(); if (b != null) { final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); final MotionEvent cancelEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(now, now, MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0); if (notifyOnInterceptTouchEvent) { //调用Behavior的onInterceptTouchEvent方法,而CoordinatorLayout.Behavior中的默认实现为return false,仅仅是触发了Behavior里对应的回调而已 b.onInterceptTouchEvent(this, child, cancelEvent); } else { b.onTouchEvent(this, child, cancelEvent); } cancelEvent.recycle(); } } for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { final View child = getChildAt(i); final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); lp.resetTouchBehaviorTracking(); } mBehaviorTouchView = null; mDisallowInterceptReset = false; } private boolean performIntercept(MotionEvent ev, final int type) { boolean intercepted = false; boolean newBlock = false; MotionEvent cancelEvent = null; final int action = ev.getActionMasked(); final List<View> topmostChildList = mTempList1; //用当前的子视图填充列表,并对其进行排序,以使z顺序中的最高视图位于列表的前面。 getTopSortedChildren(topmostChildList); final int childCount = topmostChildList.size(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { final View child = topmostChildList.get(i); final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); final Behavior b = lp.getBehavior(); if ((intercepted || newBlock) && action != MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) { // Cancel all behaviors beneath the one that intercepted.If the event is "down" then we don't have anything to cancel yet. if (b != null) { if (cancelEvent == null) { final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); cancelEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(now, now, MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0); } switch (type) { case TYPE_ON_INTERCEPT: b.onInterceptTouchEvent(this, child, cancelEvent); break; case TYPE_ON_TOUCH: b.onTouchEvent(this, child, cancelEvent); break; } } continue; } //第一次执行时Behavior不为空且intercepted未false时 if (!intercepted && b != null) { switch (type) { case TYPE_ON_INTERCEPT: // intercepted = b.onInterceptTouchEvent(this, child, ev); break; case TYPE_ON_TOUCH: intercepted = b.onTouchEvent(this, child, ev); break; } //设置了Behavior的View 赋值给mBehaviorTouchView if (intercepted) { mBehaviorTouchView = child; } } ... } topmostChildList.clear(); return intercepted; } @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { boolean handled = false; boolean cancelSuper = false; MotionEvent cancelEvent = null; final int action = ev.getActionMasked(); //mBehaviorTouchView 是当Behavior对应方法返回true时在performIntercept方法里被赋值的,是设置了Behavior的View if (mBehaviorTouchView != null || (cancelSuper = performIntercept(ev, TYPE_ON_TOUCH))) { // Safe since performIntercept guarantees that mBehaviorTouchView != null if it returns true final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) mBehaviorTouchView.getLayoutParams(); final Behavior b = lp.getBehavior(); if (b != null) { handled = b.onTouchEvent(this, mBehaviorTouchView, ev); } } // Keep the super implementation correct if (mBehaviorTouchView == null) { handled |= super.onTouchEvent(ev); } else if (cancelSuper) { if (cancelEvent == null) { final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); cancelEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(now, now, MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0); } super.onTouchEvent(cancelEvent); } ... if (cancelEvent != null) { cancelEvent.recycle(); } if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP || action == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL) { resetTouchBehaviors(false); } return handled; } 4、在CoordinatorLayout的onMeasure方法遍历查找子View并建立“主题——观察者”联系
@Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { prepareChildren(); ensurePreDrawListener(); ... final int paddingLeft = getPaddingLeft(); final int layoutDirection = ViewCompat.getLayoutDirection(this); final boolean isRtl = layoutDirection == ViewCompat.LAYOUT_DIRECTION_RTL; final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); final int childCount = mDependencySortedChildren.size(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { final View child = mDependencySortedChildren.get(i); ///Visibility为GONE时,是不能建立联系的 if (child.getVisibility() == GONE) { continue; } final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); int keylineWidthUsed = 0; ... //获取Behavior final Behavior b = lp.getBehavior(); //执行Behavior的onMeasureChild方法 if (b == null || !b.onMeasureChild(this, child, childWidthMeasureSpec, keylineWidthUsed, childHeightMeasureSpec, 0)) { onMeasureChild(child, childWidthMeasureSpec, keylineWidthUsed, childHeightMeasureSpec, 0); } } ... setMeasuredDimension(width, height); } private void prepareChildren() { mDependencySortedChildren.clear(); mChildDag.clear(); for (int i = 0, count = getChildCount(); i < count; i++) { final View view = getChildAt(i); final LayoutParams lp = getResolvedLayoutParams(view); lp.findAnchorView(this, view); mChildDag.addNode(view); // Now iterate again over the other children, adding any dependencies to the graph for (int j = 0; j < count; j++) { if (j == i) { continue; } final View other = getChildAt(j); // 查找View和other之间是否存在联系 if (lp.dependsOn(this, view, other)) { //添加到mChildDag下对应的节点 if (!mChildDag.contains(other)) { mChildDag.addNode(other); } mChildDag.addEdge(other, view); } } } // Finally add the sorted graph list to our list mDependencySortedChildren.addAll(mChildDag.getSortedList()); ... } boolean dependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent, View child, View dependency) { return dependency == mAnchorDirectChild || shouldDodge(dependency, ViewCompat.getLayoutDirection(parent)) || (mBehavior != null && mBehavior.layoutDependsOn(parent, child, dependency)); } 5、CoordinatorLayout的onChildViewsChanged
final void onChildViewsChanged(@DispatchChangeEvent final int type) { final int layoutDirection = ViewCompat.getLayoutDirection(this); final int childCount = mDependencySortedChildren.size(); final Rect inset = acquireTempRect(); for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) { final View child = mDependencySortedChildren.get(i); final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); if (type == EVENT_PRE_DRAW && child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) { // Do not try to update GONE child views in pre draw updates. continue; } // Check child views before for anchor for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { //从前面集合中拿到观察者View final View checkChild = mDependencySortedChildren.get(j); if (lp.mAnchorDirectChild == checkChild) { offsetChildToAnchor(child, layoutDirection); } } ... // Update any behavior-dependent views for the change for (int j = i + 1; j < childCount; j++) { final View checkChild = mDependencySortedChildren.get(j); final LayoutParams checkLp = (LayoutParams) checkChild.getLayoutParams(); final Behavior b = checkLp.getBehavior(); if (b != null && b.layoutDependsOn(this, checkChild, child)) { if (type == EVENT_PRE_DRAW && checkLp.getChangedAfterNestedScroll()) { // If this is from a pre-draw and we have already been changed from a nested scroll, skip the dispatch and reset the flag checkLp.resetChangedAfterNestedScroll(); continue; } final boolean handled; switch (type) { case EVENT_VIEW_REMOVED: // EVENT_VIEW_REMOVED means that we need to dispatch // onDependentViewRemoved() instead b.onDependentViewRemoved(this, checkChild, child); handled = true; break; default: // Otherwise we dispatch onDependentViewChanged() handled = b.onDependentViewChanged(this, checkChild, child); break; } } } } ... }
本网页所有视频内容由 imoviebox边看边下-网页视频下载, iurlBox网页地址收藏管理器 下载并得到。
ImovieBox网页视频下载器 下载地址: ImovieBox网页视频下载器-最新版本下载
本文章由: imapbox邮箱云存储,邮箱网盘,ImageBox 图片批量下载器,网页图片批量下载专家,网页图片批量下载器,获取到文章图片,imoviebox网页视频批量下载器,下载视频内容,为您提供.
阅读和此文章类似的: 全球云计算
 官方软件产品操作指南 (170)
官方软件产品操作指南 (170)